Upper East Side Orthodontics
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Upper East Side Orthodontics, located in the vibrant city of New York, New York, is dedicated to providing top-quality orthodontic care in a welcoming and comfortable environment. Led by a team of experienced orthodontists, our practice combines advanced technology with personalized treatment plans to help patients achieve the smiles they’ve always dreamed of. Whether you’re considering traditional braces or clear aligners, Upper East Side Orthodontics offers a comprehensive range of orthodontic services tailored to your unique needs.
Orthodontic Services
Traditional Braces
- Metal Braces: Time-tested orthodontic solution for correcting misaligned teeth and bite issues.
- Ceramic Braces: Clear or tooth-colored brackets for a more discreet orthodontic treatment option.
Clear Aligner Therapy
- Invisalign: Removable clear aligners for a virtually invisible way to straighten teeth without traditional braces.
- ClearCorrect: Transparent aligners that gradually shift teeth into alignment for a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
Comprehensive Orthodontic Care
Initial Consultation
- Orthodontic Evaluation: Thorough assessment to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your individual orthodontic needs.
- Customized Treatment Plan: Tailored orthodontic approach designed to achieve optimal results while considering your lifestyle and preferences.
Orthodontic Treatment
- Braces Adjustment: Regular visits to ensure braces or aligners are properly adjusted for consistent progress and comfort.
- Interceptive Orthodontics: Early intervention to address orthodontic issues in children and guide proper jaw and tooth development.
Patient Experience
Comfortable Environment
- Modern Facility: State-of-the-art office equipped with the latest orthodontic technology for efficient and effective treatment.
- Relaxing Atmosphere: Comfortable and inviting environment to help patients feel at ease during their orthodontic appointments.
Personalized Care
- Individualized Attention: Dedicated orthodontic team committed to providing personalized care and addressing your specific concerns throughout your treatment journey.
- Open Communication: Transparent communication about your treatment plan, progress, and any adjustments needed to ensure the best possible outcome.
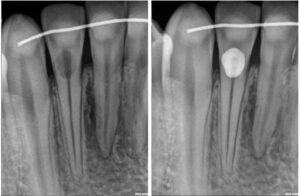
Root Resorption
Root resorption is a pathological process characterized by the breakdown or loss of dentin, cementum, and/or bone in the root of a tooth. It can occur as a result of various factors and may involve either external resorption, which affects the outer surface of the root, or internal resorption, which affects the pulp chamber and root canal system within the tooth.
Here are some key points about root resorption:
- Types of Root Resorption:
- External Resorption: External resorption, also known as external inflammatory resorption, typically occurs in response to trauma, orthodontic treatment, periodontal disease, or excessive mechanical forces. It involves the breakdown of cementum and dentin on the outer surface of the root and may progress slowly over time if left untreated.
- Internal Resorption: Internal resorption, also known as internal inflammatory resorption, occurs within the pulp chamber and root canal system of the tooth. It can be caused by trauma, chronic pulp inflammation, pulpal necrosis, or excessive orthodontic forces. Internal resorption is often asymptomatic and may be detected incidentally on dental radiographs.
- Causes of Root Resorption:
- Trauma: Dental trauma, such as falls, sports injuries, or accidents, can lead to root resorption, particularly if the tooth sustains a significant impact or fracture.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Orthodontic forces applied during tooth movement can sometimes lead to localized areas of root resorption, particularly in cases of prolonged or excessive force application.
- Periodontal Disease: Advanced periodontal disease or inflammation can cause destruction of the supporting structures of the tooth, leading to root resorption.
- Pulpal Pathology: Chronic pulp inflammation, pulp necrosis, or periapical infection can initiate internal resorption within the pulp chamber and root canal system.
- Clinical Presentation:
- External resorption may present with symptoms such as tooth mobility, sensitivity to percussion or palpation, localized swelling, or changes in tooth position.
- Internal resorption is often asymptomatic and may be detected incidentally on dental radiographs during routine dental examinations.
- Severe or advanced cases of root resorption may lead to tooth fracture, pulp exposure, or loss of tooth vitality.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of root resorption involves a comprehensive clinical examination, assessment of dental history, and evaluation of dental radiographs or imaging studies.
- Dental radiographs, including periapical radiographs or cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), are essential for visualizing the extent and location of root resorption and determining appropriate treatment options.
- Treatment:
- The treatment approach for root resorption depends on the cause, extent, and severity of the resorption.
- In cases of external resorption, treatment may involve stabilization of the tooth, elimination of causative factors (e.g., orthodontic forces), and surgical intervention to remove affected tissue and restore the root structure.
- Internal resorption may require endodontic treatment (root canal therapy) to remove necrotic tissue, disinfect the root canal system, and seal the resorptive defect with biocompatible materials.
- Severe or advanced cases of root resorption may necessitate tooth extraction followed by replacement with a dental implant, bridge, or removable prosthesis.
In summary, root resorption is a pathological process characterized by the breakdown or loss of dentin, cementum, and/or bone in the root of a tooth. It can occur due to various factors such as trauma, orthodontic treatment, periodontal disease, or pulpal pathology. Diagnosis and treatment of root resorption require a thorough evaluation and may involve stabilization of the tooth, removal of causative factors, endodontic treatment, or tooth extraction followed by replacement with a dental prosthesis. Early detection and intervention are essential for preserving tooth structure and function and preventing complications associated with root resorption.
Tooth Reshaping
Tooth reshaping, also known as dental contouring or enameloplasty, is a cosmetic dental procedure aimed at improving the appearance of teeth by altering their shape, size, or surface contour. It involves the removal or modification of small amounts of tooth enamel to achieve desired aesthetic results. Tooth reshaping is often used to correct minor imperfections, enhance symmetry, and create a more harmonious smile. Here's an overview of tooth reshaping and its key aspects:
- Indications for Tooth Reshaping:
- Tooth reshaping may be recommended for patients with the following cosmetic concerns:
- Irregular tooth shape or size, such as pointed or jagged edges.
- Minor chips, fractures, or enamel wear.
- Overlapping or uneven teeth.
- Pits, grooves, or rough surfaces on tooth enamel.
- Small imperfections affecting the appearance of the smile.
- Preoperative Evaluation:
- Before tooth reshaping, the dentist will conduct a thorough dental examination to assess the patient's oral health, identify cosmetic concerns, and discuss treatment goals. Dental X-rays or digital scans may be taken to evaluate tooth structure and plan the reshaping process.
- Treatment Planning:
- Based on the patient's needs and preferences, the dentist will develop a customized treatment plan outlining the areas of the teeth to be reshaped and the desired changes in tooth contour. Digital smile design software or mock-up models may be used to visualize the anticipated results and guide the reshaping process.
- Tooth Reshaping Procedure:
- Tooth reshaping is typically performed as an outpatient procedure and does not require anesthesia in most cases, as only minimal enamel removal is involved. The steps of the procedure may include:
- Marking: The dentist marks the areas of the teeth to be reshaped using dental markers or cosmetic pencils, taking into account the desired changes in tooth contour.
- Enamel Removal: Using specialized dental instruments, such as drills, burrs, or abrasive discs, the dentist carefully removes small amounts of enamel from the tooth surfaces to achieve the desired shape and contour. The process is precise and controlled to ensure optimal results while preserving tooth structure and integrity.
- Smoothing and Polishing: After reshaping the teeth, the dentist smooths and refines the tooth surfaces to eliminate rough edges, create a uniform appearance, and enhance the natural luster of the enamel. Polishing may be performed using fine-grit polishing disks or dental polishing pastes to achieve a smooth, glossy finish.
- Postoperative Care and Recovery:
- Following tooth reshaping, patients are typically able to resume normal activities immediately, as the procedure is minimally invasive and involves minimal discomfort. However, some individuals may experience mild tooth sensitivity or discomfort, which usually resolves within a few days.
- Patients are advised to practice good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, to maintain the health and appearance of reshaped teeth. Avoiding habits that can damage tooth enamel, such as teeth grinding or biting hard objects, is also recommended to preserve the results of tooth reshaping.
- Long-Term Results:
- The results of tooth reshaping are generally permanent, as the changes made to the tooth structure are irreversible. With proper care and maintenance, reshaped teeth can provide long-lasting improvements in smile aesthetics and boost self-confidence. However, it's important for patients to communicate with their dentist if they have any concerns or if further refinements are desired.
In summary, tooth reshaping is a conservative and effective cosmetic dental procedure used to enhance the appearance of teeth by modifying their shape, size, or surface texture. By carefully contouring tooth enamel, dentists can address minor imperfections and create a more attractive and harmonious smile for their patients.