Park Avenue Orthodontics
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Park Avenue Orthodontics, nestled in the heart of New York, New York, is committed to providing exceptional orthodontic care in a modern and comfortable setting. Led by a team of skilled orthodontists, our practice combines cutting-edge technology with personalized treatment plans to help patients achieve beautiful and healthy smiles. Whether you’re seeking traditional braces or clear aligners, Park Avenue Orthodontics offers a comprehensive range of orthodontic services tailored to your individual needs.
Orthodontic Services
Traditional Braces
- Metal Braces: Time-tested orthodontic solution for correcting misaligned teeth and bite issues.
- Ceramic Braces: Clear or tooth-colored brackets for a more discreet orthodontic treatment option.
Clear Aligner Therapy
- Invisalign: Removable clear aligners for a virtually invisible way to straighten teeth without traditional braces.
- ClearCorrect: Transparent aligners that gradually shift teeth into alignment for a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
Comprehensive Orthodontic Care
Initial Consultation
- Orthodontic Evaluation: Thorough assessment to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your unique orthodontic needs.
- Customized Treatment Plan: Tailored orthodontic approach designed to achieve optimal results while considering your lifestyle and preferences.
Orthodontic Treatment
- Braces Adjustment: Regular visits to ensure braces or aligners are properly adjusted for consistent progress and comfort.
- Interceptive Orthodontics: Early intervention to address orthodontic issues in children and guide proper jaw and tooth development.
Patient Experience
Comfortable Environment
- Modern Facility: State-of-the-art office equipped with the latest orthodontic technology for efficient and effective treatment.
- Relaxing Atmosphere: Comfortable and inviting environment to help patients feel at ease during their orthodontic appointments.
Personalized Care
- Individualized Attention: Dedicated orthodontic team committed to providing personalized care and addressing your specific concerns throughout your treatment journey.
- Open Communication: Transparent communication about your treatment plan, progress, and any adjustments needed to ensure the best possible outcome.
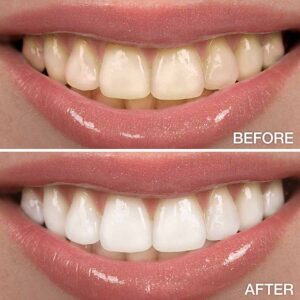
Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening, also known as teeth bleaching, is a popular cosmetic dental procedure designed to lighten the color of the teeth and remove stains or discoloration. It is a non-invasive treatment that can enhance the appearance of the smile by creating a brighter, whiter, and more youthful-looking smile. Here's an overview of teeth whitening and its key aspects:
- Purpose of Teeth Whitening:
- Teeth whitening is primarily aimed at improving the aesthetic appearance of the teeth by lightening their shade and removing surface stains caused by various factors, including:
- Consumption of staining foods and beverages (e.g., coffee, tea, red wine).
- Tobacco use (smoking or chewing tobacco).
- Aging, which can lead to natural yellowing or darkening of the teeth.
- Poor oral hygiene habits that result in plaque buildup and surface discoloration.
- Certain medications or medical conditions that affect tooth coloration.
- Types of Teeth Whitening:
- In-Office Whitening: Professional teeth whitening treatments performed in a dental office under the supervision of a dentist. In-office whitening procedures typically involve the application of a high-concentration bleaching agent (e.g., hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide) to the teeth, which is activated by a special light or laser to accelerate the whitening process. In-office whitening offers fast and dramatic results, often achieving several shades of whitening in a single appointment.
- At-Home Whitening: Take-home whitening kits provided by a dentist for use in the comfort of your own home. These kits include custom-fitted whitening trays or strips filled with a lower-concentration bleaching gel, which is worn over the teeth for a specified period (usually a few hours each day or overnight) over the course of several days to weeks. At-home whitening kits offer a more gradual but equally effective approach to whitening and are ideal for individuals who prefer the convenience and flexibility of whitening at their own pace.
- Treatment Process:
- In-Office Whitening: The dentist begins by protecting the gums and soft tissues with a protective barrier or dental dam to minimize the risk of irritation or sensitivity. The bleaching agent is then applied to the teeth and activated with a light source to initiate the whitening process. The gel is left on the teeth for a specific duration, during which it penetrates the enamel to break down stains and discoloration. Multiple cycles of bleaching may be performed as needed to achieve the desired level of whitening.
- At-Home Whitening: The dentist takes impressions of your teeth to create custom-fitted whitening trays that conform snugly to your dental arches. You are provided with the whitening trays, along with the bleaching gel and instructions for use. To use the at-home whitening kit, you fill the trays with the bleaching gel and wear them over your teeth for the prescribed amount of time each day. The whitening process typically takes several days to weeks to achieve noticeable results.
- Safety and Effectiveness:
- Professional teeth whitening treatments performed by a qualified dentist are considered safe and effective when administered according to professional guidelines and manufacturer instructions.
- While teeth whitening is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience temporary tooth sensitivity or gum irritation during or after treatment. These side effects typically resolve on their own and can be managed with desensitizing toothpaste or other remedies recommended by your dentist.
- It's important to consult with a dentist before undergoing teeth whitening to ensure that you are a suitable candidate for treatment and to discuss any concerns or expectations you may have.
- Maintenance and Longevity:
- The duration of teeth whitening results can vary depending on individual factors such as oral hygiene habits, dietary choices, and lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking). In general, teeth whitening effects may last from several months to several years.
- To prolong the results of teeth whitening and maintain a bright, healthy smile, it's important to:
- Practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly to remove plaque and surface stains.
- Limit consumption of staining foods and beverages or rinse your mouth with water after consuming them.
- Avoid tobacco use, which can cause tooth discoloration and compromise whitening results.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to monitor oral health and touch up whitening treatments as needed.
In summary, teeth whitening is a safe, effective, and non-invasive cosmetic dental procedure that can enhance the appearance of your smile by brightening and rejuvenating the natural color of your teeth. Whether performed in a dental office or at home, teeth whitening offers a convenient and reliable solution for achieving a whiter, more radiant smile and boosting your confidence in your appearance.
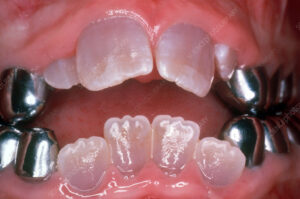
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI) is a hereditary genetic disorder that affects the development and formation of dentin, one of the primary tissues that make up teeth. It is characterized by abnormal dentin structure and composition, leading to weakened and discolored teeth that are prone to fracture, wear, and sensitivity. Dentinogenesis imperfecta is typically inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, meaning that a child has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition if one of their parents carries the mutated gene.
Here are some key points about dentinogenesis imperfecta:
- Types: Dentinogenesis imperfecta is classified into three main types based on clinical and genetic features:
- Type I: Also known as classic or hereditary opalescent dentinogenesis imperfecta, this type is the most common and severe form of the condition. It is characterized by translucent or opalescent (bluish-gray) teeth with bulbous crowns, narrow roots, and severe attrition (wear) of the enamel. Type I DI is caused by mutations in the DSPP (dentin sialophosphoprotein) gene, which encodes a protein involved in dentin formation.
- Type II: Also known as coronal dentinogenesis imperfecta, this type is characterized by similar dental abnormalities as type I DI but with less severe enamel involvement. Teeth may appear yellow-brown or amber in color and may be more resistant to fracture compared to type I DI. Type II DI is also caused by mutations in the DSPP gene.
- Type III: Also known as Brandywine type dentinogenesis imperfecta, this type is characterized by similar dental abnormalities as type II DI but with additional skeletal abnormalities such as short stature and joint laxity. Type III DI is caused by mutations in the DSPP gene as well.
- Clinical Presentation: Dentinogenesis imperfecta typically presents with a distinctive appearance of the teeth, including opalescent or discolored enamel, bulbous crowns, and attrition of the enamel exposing the underlying dentin. The teeth may appear translucent or amber in color, and the enamel may chip or fracture easily due to its weakened structure. Individuals with dentinogenesis imperfecta may also experience dental sensitivity, pulp exposure, and increased risk of dental caries and infections.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis of dentinogenesis imperfecta is based on clinical and radiographic findings, including characteristic dental abnormalities such as opalescent or discolored enamel, bulbous crowns, and narrowed pulp chambers. Dental X-rays may reveal thin and bulbous roots, obliteration of the pulp chambers, and dentin defects such as taurodontism (enlarged pulp chambers) or pulpal calcifications. Genetic testing may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and identify the underlying genetic mutation responsible for the condition.
- Treatment: Treatment of dentinogenesis imperfecta focuses on preserving tooth structure, preventing complications, and improving oral function and aesthetics. Management options may include dental restorations such as crowns, veneers, or composite fillings to protect and reinforce weakened teeth, extraction of severely affected teeth followed by prosthetic replacement, endodontic therapy (root canal treatment) for teeth with pulp exposure or infection, and preventive measures such as fluoride therapy and meticulous oral hygiene to reduce the risk of dental caries and infections.
In summary, dentinogenesis imperfecta is a hereditary genetic disorder characterized by abnormal development and structure of dentin, resulting in weakened and discolored teeth that are prone to fracture, wear, and sensitivity. Early diagnosis and appropriate dental management are essential for preserving tooth structure, preventing complications, and improving oral function and aesthetics in individuals with dentinogenesis imperfecta.