Immediate Dental Service
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Immediate Dental Service, located in the heart of New York, New York, is your go-to destination for prompt and efficient dental care when you need it most. With a commitment to providing immediate relief and solutions for dental emergencies, the practice offers a comprehensive range of urgent dental services in a convenient and accessible location. Led by a team of experienced emergency dentists, Immediate Dental Service strives to deliver high-quality care with minimal wait times, ensuring that patients receive the attention they need when experiencing dental pain or discomfort.
Urgent Dental Services
Emergency Examinations
- Rapid Assessments: Immediate evaluations to diagnose dental emergencies and determine the appropriate course of action.
- Pain Management: Quick relief from dental pain through various techniques, including local anesthesia and sedation options.
Emergency Dental Treatments
- Emergency Extractions: Prompt removal of severely damaged or infected teeth causing acute pain or discomfort.
- Emergency Root Canal Therapy: Expedited root canal treatment to alleviate pain and save infected teeth.
Immediate Care
Same-Day Appointments
- Flexible Scheduling: Accommodating same-day appointments for patients experiencing dental emergencies.
- Walk-In Services: Convenient walk-in availability for urgent dental care without the need for a prior appointment.
Efficient Treatment
- Rapid Response: Prompt attention from experienced emergency dentists to address urgent dental needs without delay.
- Streamlined Procedures: Expedited processes to minimize waiting times and efficiently manage dental emergencies.
Patient Care
Compassionate Approach
- Empathetic Staff: Caring and supportive dental professionals dedicated to providing comfort and reassurance during stressful situations.
- Clear Communication: Transparent explanations of treatment options and expectations to empower patients to make informed decisions about their dental care.
Aftercare Support
- Post-Treatment Guidance: Clear instructions and guidance on managing post-procedure discomfort and maintaining oral health following emergency dental treatments.
- Follow-Up Care: Scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure the successful resolution of dental emergencies and address any lingering concerns.
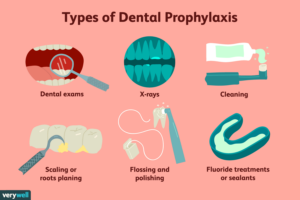
Prophylaxis
Dental prophylaxis, commonly referred to as a dental cleaning, is a preventive dental procedure performed by a dental hygienist or dentist to remove plaque, tartar (calculus), and stains from the teeth and gums. It plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal oral health and preventing dental problems such as tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath. Here's an overview of dental prophylaxis and its importance:
- Plaque and Tartar Removal:
- Dental prophylaxis involves the thorough removal of plaque and tartar buildup from the tooth surfaces, especially along the gumline and between the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth throughout the day and can harden into tartar if not removed through regular brushing and flossing. Tartar is a hardened deposit that cannot be removed with regular brushing and requires professional intervention to prevent dental problems.
- Prevention of Tooth Decay and Gum Disease:
- By removing plaque and tartar, dental prophylaxis helps prevent the development of tooth decay (cavities) and gum disease (periodontal disease). Plaque bacteria produce acids that can erode tooth enamel and lead to cavities, while tartar buildup along the gumline can irritate the gums and contribute to gum inflammation and infection. Regular dental cleanings help keep the teeth and gums healthy and reduce the risk of dental problems.
- Detection of Oral Health Issues:
- During a dental cleaning, the dental hygienist or dentist will also perform a thorough examination of the teeth, gums, and oral tissues to detect any signs of dental problems or oral health issues. This may include checking for signs of tooth decay, gum inflammation, oral cancer, or other abnormalities. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing the progression of oral health issues and maintaining overall oral health.
- Fresh Breath:
- Dental prophylaxis can also help improve and maintain fresh breath by removing plaque, tartar, and bacteria that contribute to bad breath (halitosis). Cleaning the teeth and gums thoroughly can eliminate odor-causing bacteria and leave the mouth feeling clean and refreshed.
- Promotion of Overall Health:
- Research has shown that there is a strong link between oral health and overall health, with poor oral hygiene being associated with an increased risk of systemic health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections. By maintaining good oral hygiene habits and scheduling regular dental cleanings, individuals can help protect their overall health and well-being.
Overall, dental prophylaxis is an essential component of preventive dental care that helps keep the teeth and gums healthy, prevents dental problems, and promotes overall oral and systemic health. It is recommended that individuals undergo dental cleanings at least every six months, or as recommended by their dentist, to maintain optimal oral health and prevent the need for more extensive dental treatment in the future.
Bone Density Evaluation
Bone density evaluation, also known as bone density testing or bone densitometry, is a medical procedure used to measure the strength and density of bones, typically in the hip, spine, or forearm. This assessment helps healthcare providers diagnose osteoporosis, assess fracture risk, and monitor the effectiveness of treatment for bone-related conditions. Here's an overview of bone density evaluation:
- Indications:
- Bone density evaluation is recommended for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or fractures, including postmenopausal women, older adults, individuals with a family history of osteoporosis, and those with certain medical conditions or taking medications that affect bone health.
- It may also be recommended for individuals who have experienced a fracture or have other risk factors for osteoporosis, such as low body weight, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or a sedentary lifestyle.
- Bone Densitometry Techniques:
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA): This is the most commonly used technique for measuring bone density. It involves using low-dose X-rays to scan the hip, spine, or forearm and assess bone mineral density (BMD). DXA scans are quick, non-invasive, and provide precise measurements of bone density.
- Quantitative ultrasound (QUS): This technique measures bone density using sound waves instead of X-rays. It is often used as a screening tool and may be performed at the heel or wrist.
- Peripheral dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (pDXA): This portable device measures bone density at peripheral sites such as the wrist, heel, or finger.
- Preparation:
- Preparation for a bone density evaluation is typically minimal. Patients may be advised to wear loose, comfortable clothing and avoid wearing metal objects or jewelry that may interfere with the scan.
- In some cases, patients may be instructed to refrain from taking calcium supplements or certain medications prior to the test, as they can affect the results.
- Procedure:
- During a DXA scan, the patient lies on a table while a scanner arm passes over the body, emitting low-dose X-rays. The procedure is painless and usually takes about 10 to 30 minutes to complete.
- For QUS or pDXA, the patient may be asked to place the body part being scanned (such as the heel or wrist) against a small device that emits sound waves or X-rays.
- Interpretation of Results:
- The results of the bone density evaluation are typically reported as a T-score, which compares the patient's bone density to that of a healthy young adult of the same gender. A T-score of -1 or above is considered normal, while scores between -1 and -2.5 indicate low bone density (osteopenia), and scores below -2.5 indicate osteoporosis.
- The healthcare provider will interpret the results of the bone density evaluation in conjunction with other clinical factors, such as age, gender, medical history, and fracture risk, to assess the patient's overall bone health and determine appropriate management strategies.
- Follow-up and Monitoring:
- Depending on the results of the bone density evaluation, the healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, weight-bearing exercises, and/or medications to help maintain or improve bone health.
- Follow-up bone density evaluations may be recommended periodically to monitor changes in bone density over time and assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
Bone density evaluation is a valuable tool for assessing bone health, diagnosing osteoporosis, and guiding treatment decisions to reduce fracture risk and improve overall bone health. If you are at risk of osteoporosis or fractures, or if you have concerns about your bone health, it's important to discuss with your healthcare provider whether a bone density evaluation is appropriate for you.