New York Endodontic Associates
Contact
Hours
<ul id=”hours” style=”transition: height .3s ease;”>
<li>Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm</li>
<li>Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm</li>
</ul>
New York Endodontic Associates, located in the bustling city of New York, NY, is a leading practice specializing in endodontic care. The practice is dedicated to providing exceptional root canal therapy and other endodontic treatments in a comfortable and compassionate environment. Led by a team of experienced endodontists, New York Endodontic Associates offers state-of-the-art procedures to save natural teeth and relieve dental pain.
Endodontic Services
Root Canal Therapy
- Expert Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis of dental pain and identification of the cause to determine the need for root canal treatment.
- Precision Treatment: State-of-the-art techniques and equipment to perform root canal therapy with precision and efficiency.
- Gentle Care: Compassionate approach to alleviate dental anxiety and ensure a comfortable experience for every patient.
Endodontic Surgery
- Apicoectomy: Surgical procedure to remove infected tissue and seal the root tip, often performed when conventional root canal therapy is not sufficient.
- Root Canal Retreatment: Revision of a previous root canal treatment to address persistent infection or other complications.
Advanced Procedures
Microscopic Endodontics
- High-Powered Microscopes: Utilization of advanced microscopes for enhanced visualization and precision during root canal procedures.
- Ultrasonic Instrumentation: Gentle and efficient removal of infected tissue using ultrasonic technology, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Regenerative Endodontics
- Pulpotomy: Partial removal of damaged pulp tissue followed by application of regenerative materials to promote healing and preserve tooth vitality.
- Revascularization: Stimulating the growth of new blood vessels and tissues inside the tooth to revitalize damaged or infected pulp.
Patient Care
Comprehensive Consultations
- Thorough Examinations: Detailed evaluations and discussions to educate patients about their treatment options and address any concerns.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Customized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique oral health needs and goals.
Comfort and Support
- Relaxing Environment: A calming atmosphere designed to help patients feel at ease during their visits.
- Pain Management: Utilization of advanced anesthesia techniques to minimize discomfort during procedures.
Bruxism
Bruxism is a condition characterized by involuntary, excessive grinding, clenching, or gnashing of the teeth, often during sleep. It can lead to a range of symptoms and dental problems, including tooth wear, jaw pain, headaches, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Bruxism can be classified into awake bruxism, which occurs during waking hours, and sleep bruxism, which occurs during sleep.
Here are some key points about bruxism:
- Causes:
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional stress or tension can contribute to bruxism, leading individuals to clench or grind their teeth as a coping mechanism.
- Malocclusion: Misalignment of the teeth or jaws can cause an uneven bite, prompting the body to adjust by grinding or clenching the teeth.
- Sleep disorders: Bruxism may be associated with sleep-related conditions such as sleep apnea, snoring, or periodic limb movements.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, stimulants, or antipsychotics, can increase the risk of bruxism as a side effect.
- Lifestyle factors: Excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, smoking, or recreational drug use may exacerbate bruxism.
- Genetic factors: There may be a genetic predisposition to bruxism, as it tends to run in families.
- Symptoms:
- Tooth wear: Bruxism can lead to flattening, chipping, or fracturing of the teeth, particularly the chewing surfaces.
- Jaw pain or stiffness: Excessive clenching or grinding can strain the muscles of the jaw, leading to discomfort, tension, or difficulty opening or closing the mouth.
- Headaches: Bruxism-related muscle tension and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction can cause headaches, particularly upon waking in the morning.
- Ear pain: Bruxism-related muscle tension can radiate to the ears, causing pain, ringing (tinnitus), or ear congestion.
- Sleep disturbances: Bruxism may disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fragmented or poor-quality sleep for both the individual and their sleep partner.
- Tooth sensitivity: Grinding can wear down the protective enamel layer of the teeth, increasing sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of bruxism is typically based on clinical evaluation, dental examination, and patient history.
- Your dentist may look for signs of tooth wear, muscle tenderness, or TMJ dysfunction during a dental examination.
- In some cases, your dentist may recommend additional tests such as electromyography (EMG) to measure muscle activity or polysomnography (sleep study) to assess sleep-related bruxism.
- Treatment:
- Treatment of bruxism aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent further dental damage, and address underlying causes. Treatment options may include:
- Occlusal splints or mouthguards: Custom-fitted oral appliances worn during sleep can protect the teeth from grinding and reduce muscle tension.
- Stress management techniques: Relaxation techniques, mindfulness, counseling, or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals manage stress and reduce bruxism-related symptoms.
- Behavioral therapies: Biofeedback, habit-reversal techniques, or hypnosis may be effective in modifying bruxism behaviors.
- Medications: Muscle relaxants, antidepressants, or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed in severe cases to alleviate muscle tension or anxiety-related bruxism.
- Dental treatments: Restorative procedures such as dental crowns, overlays, or composite bonding may be necessary to repair damaged teeth and restore proper occlusion.
- Prevention:
- To prevent bruxism or minimize its impact, it's important to:
- Practice good stress management techniques, such as regular exercise, relaxation exercises, or mindfulness meditation.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, or recreational drugs, which can exacerbate bruxism symptoms.
- Maintain good sleep hygiene habits, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime.
- Seek treatment for underlying medical conditions or sleep disorders that may contribute to bruxism, such as sleep apnea or restless legs syndrome.
In summary, bruxism is a common condition characterized by involuntary grinding or clenching of the teeth, often during sleep. It can lead to a range of symptoms and dental problems, including tooth wear, jaw pain, headaches, and TMJ disorders. Treatment options for bruxism focus on alleviating symptoms, preventing further dental damage, and addressing underlying causes such as stress, malocclusion, or sleep disorders. If you suspect you have bruxism or experience symptoms such as tooth wear, jaw pain, or headaches, it's important to consult your dentist for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
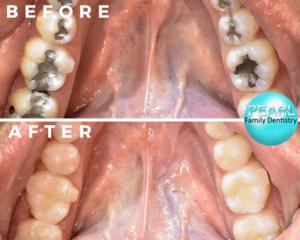
Filling Replacement
Dental filling replacement is a procedure aimed at replacing old or damaged dental fillings with new materials to restore the integrity and functionality of the affected teeth. Over time, dental fillings may wear down, become discolored, or develop cracks, which can compromise their effectiveness and lead to further dental problems if left untreated.
During a dental filling replacement procedure, the dentist will first assess the condition of the existing fillings through visual inspection and dental imaging techniques such as X-rays. If the fillings are found to be deteriorating or failing, the dentist will recommend their replacement.
The process typically involves the following steps:
- Removal of Old Fillings: The dentist will carefully remove the old fillings using dental instruments such as drills or ultrasonic scalers. This process may involve the removal of any decayed or damaged tooth structure surrounding the filling.
- Preparation of Tooth: Once the old fillings are removed, the tooth is cleaned and prepared to receive the new filling material. This may involve shaping the tooth and removing any remaining decay or debris.
- Placement of New Filling: The dentist will select an appropriate filling material based on the location and extent of the restoration needed. Common filling materials include composite resin, amalgam, porcelain, and gold. The chosen material is then placed and shaped to restore the natural contour and function of the tooth.
- Finishing and Polishing: After the new filling is placed, the dentist will carefully polish it to ensure a smooth and natural-looking surface. This helps to improve the aesthetics of the restoration and minimize the risk of plaque accumulation and staining.
- Evaluation: Once the procedure is complete, the dentist will evaluate the new filling to ensure proper fit, function, and occlusion. Any necessary adjustments may be made to achieve optimal results.
Replacing old or damaged dental fillings is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing further dental problems such as decay, infection, or fracture of the tooth. By addressing deteriorating fillings promptly, patients can preserve the strength and integrity of their teeth and enjoy long-term dental wellness. Regular dental check-ups and preventive care are key to identifying and addressing filling replacement needs in a timely manner.