Central Park Periodontics
Contact
Hours
<ul id=”hours” style=”transition: height .3s ease;”>
<li>Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm</li>
<li>Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm</li>
</ul>
Central Park Periodontics, located in the vibrant city of New York, NY, is a premier periodontal practice dedicated to providing exceptional care for patients seeking periodontal treatment and dental implant therapy. Led by a team of skilled periodontists and oral surgeons, Central Park Periodontics offers state-of-the-art treatments in a warm and welcoming environment, ensuring optimal oral health and beautiful smiles for every patient.
Periodontal Services
Gum Disease Treatment
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Thorough examination and diagnosis of gum disease to determine the most effective treatment approach.
- Scaling and Root Planing: Non-surgical deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooth the tooth roots.
- Periodontal Surgery: Surgical interventions such as flap surgery and bone grafting to treat advanced gum disease and restore periodontal health.
Dental Implant Therapy
- Implant Placement: Expert placement of dental implants to replace missing teeth and provide a stable foundation for crowns, bridges, or dentures.
- Bone Grafting: Bone augmentation procedures to rebuild bone structure and enhance the success of dental implant placement.
- Implant Restoration: Customized restoration of dental implants with lifelike crowns or prosthetic teeth for a natural-looking smile.
Advanced Procedures
Soft Tissue Grafting
- Gum Grafts: Surgical procedures to augment thin or receding gum tissue and improve gum aesthetics and function.
- Connective Tissue Grafts: Techniques to restore gum tissue lost due to periodontal disease or trauma, enhancing smile aesthetics and gum health.
Cosmetic Periodontics
- Gum Contouring: Reshaping of the gumline to create a more symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing smile.
- Crown Lengthening: Surgical procedure to expose more of the tooth’s surface, enhancing the appearance of short or gummy smiles.
Patient Care
Personalized Treatment Plans
- Customized Consultations: In-depth discussions and treatment planning sessions to address each patient’s unique oral health needs and goals.
- Collaborative Approach: Working closely with patients and their referring dentists to ensure coordinated and comprehensive care.
Comfort and Convenience
- Relaxing Environment: A welcoming atmosphere designed to help patients feel at ease during their visits.
- Sedation Options: Providing sedation dentistry options to help anxious patients relax and feel comfortable during treatment.
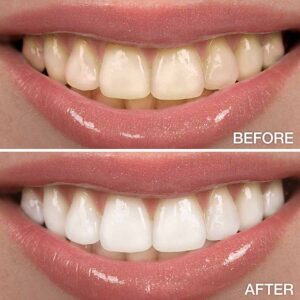
Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening, also known as teeth bleaching, is a popular cosmetic dental procedure designed to lighten the color of the teeth and remove stains or discoloration. It is a non-invasive treatment that can enhance the appearance of the smile by creating a brighter, whiter, and more youthful-looking smile. Here's an overview of teeth whitening and its key aspects:
- Purpose of Teeth Whitening:
- Teeth whitening is primarily aimed at improving the aesthetic appearance of the teeth by lightening their shade and removing surface stains caused by various factors, including:
- Consumption of staining foods and beverages (e.g., coffee, tea, red wine).
- Tobacco use (smoking or chewing tobacco).
- Aging, which can lead to natural yellowing or darkening of the teeth.
- Poor oral hygiene habits that result in plaque buildup and surface discoloration.
- Certain medications or medical conditions that affect tooth coloration.
- Types of Teeth Whitening:
- In-Office Whitening: Professional teeth whitening treatments performed in a dental office under the supervision of a dentist. In-office whitening procedures typically involve the application of a high-concentration bleaching agent (e.g., hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide) to the teeth, which is activated by a special light or laser to accelerate the whitening process. In-office whitening offers fast and dramatic results, often achieving several shades of whitening in a single appointment.
- At-Home Whitening: Take-home whitening kits provided by a dentist for use in the comfort of your own home. These kits include custom-fitted whitening trays or strips filled with a lower-concentration bleaching gel, which is worn over the teeth for a specified period (usually a few hours each day or overnight) over the course of several days to weeks. At-home whitening kits offer a more gradual but equally effective approach to whitening and are ideal for individuals who prefer the convenience and flexibility of whitening at their own pace.
- Treatment Process:
- In-Office Whitening: The dentist begins by protecting the gums and soft tissues with a protective barrier or dental dam to minimize the risk of irritation or sensitivity. The bleaching agent is then applied to the teeth and activated with a light source to initiate the whitening process. The gel is left on the teeth for a specific duration, during which it penetrates the enamel to break down stains and discoloration. Multiple cycles of bleaching may be performed as needed to achieve the desired level of whitening.
- At-Home Whitening: The dentist takes impressions of your teeth to create custom-fitted whitening trays that conform snugly to your dental arches. You are provided with the whitening trays, along with the bleaching gel and instructions for use. To use the at-home whitening kit, you fill the trays with the bleaching gel and wear them over your teeth for the prescribed amount of time each day. The whitening process typically takes several days to weeks to achieve noticeable results.
- Safety and Effectiveness:
- Professional teeth whitening treatments performed by a qualified dentist are considered safe and effective when administered according to professional guidelines and manufacturer instructions.
- While teeth whitening is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience temporary tooth sensitivity or gum irritation during or after treatment. These side effects typically resolve on their own and can be managed with desensitizing toothpaste or other remedies recommended by your dentist.
- It's important to consult with a dentist before undergoing teeth whitening to ensure that you are a suitable candidate for treatment and to discuss any concerns or expectations you may have.
- Maintenance and Longevity:
- The duration of teeth whitening results can vary depending on individual factors such as oral hygiene habits, dietary choices, and lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking). In general, teeth whitening effects may last from several months to several years.
- To prolong the results of teeth whitening and maintain a bright, healthy smile, it's important to:
- Practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly to remove plaque and surface stains.
- Limit consumption of staining foods and beverages or rinse your mouth with water after consuming them.
- Avoid tobacco use, which can cause tooth discoloration and compromise whitening results.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to monitor oral health and touch up whitening treatments as needed.
In summary, teeth whitening is a safe, effective, and non-invasive cosmetic dental procedure that can enhance the appearance of your smile by brightening and rejuvenating the natural color of your teeth. Whether performed in a dental office or at home, teeth whitening offers a convenient and reliable solution for achieving a whiter, more radiant smile and boosting your confidence in your appearance.
Epulis
Epulis is a benign growth or tumor that originates from the gum tissue. It typically appears as a firm, pinkish swelling on the gums, often near the teeth. While epulis itself is not cancerous, it can cause discomfort, especially if it grows large enough to interfere with eating or speaking. The exact cause of epulis is not always clear, but factors such as chronic irritation from dental plaque, poor oral hygiene, or certain medications may contribute to its development. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the growth, and recurrence is rare if the underlying cause, such as poor oral hygiene, is addressed. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices can help prevent the development of epulis. If you notice any unusual growths or changes in your gums, it's essential to consult a dentist for proper evaluation and treatment.