Kids Only Dental
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 1:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 1:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Kids Only Dental, located in New York, NY, is a premier pediatric dental practice dedicated exclusively to the dental needs of children. The clinic is known for its child-friendly environment, state-of-the-art facilities, and a team of highly trained animal dental professionals who provide compassionate and specialized care to ensure a positive dental experience for every child.
Dental Services
Preventive Dentistry
- Comprehensive Oral Exams: Thorough examinations to monitor and maintain oral health, with a focus on early detection of dental issues.
- Routine Cleanings: Regular cleanings to prevent cavities and promote healthy teeth and gums.
- Fluoride Treatments: Strengthening treatments to protect children’s teeth from decay.
- Dental Sealants: Protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of molars to prevent cavities.
Specialized Pediatric Dental Care
- Restorative Dentistry: Fillings and crowns to repair cavities and restore damaged teeth in children.
- Orthodontic Assessments: Early evaluations and referrals for orthodontic treatment to correct dental alignment and bite issues.
- Emergency Dental Care: Prompt and effective treatment for dental emergencies, such as toothaches, broken teeth, or dental trauma.
- Behavior Management: Techniques to help children feel comfortable and at ease during dental visits, including sedation dentistry options for anxious patients.
Educational Programs
- Oral Hygiene Education: Teaching children proper brushing and flossing techniques to encourage good oral hygiene habits.
- Nutrition Counseling: Guidance on healthy eating habits that support dental health.
- Parental Support: Resources and advice for parents to help them care for their children’s dental needs at home.
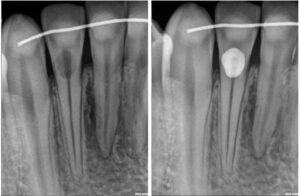
Root Resorption
Root resorption is a pathological process characterized by the breakdown or loss of dentin, cementum, and/or bone in the root of a tooth. It can occur as a result of various factors and may involve either external resorption, which affects the outer surface of the root, or internal resorption, which affects the pulp chamber and root canal system within the tooth.
Here are some key points about root resorption:
- Types of Root Resorption:
- External Resorption: External resorption, also known as external inflammatory resorption, typically occurs in response to trauma, orthodontic treatment, periodontal disease, or excessive mechanical forces. It involves the breakdown of cementum and dentin on the outer surface of the root and may progress slowly over time if left untreated.
- Internal Resorption: Internal resorption, also known as internal inflammatory resorption, occurs within the pulp chamber and root canal system of the tooth. It can be caused by trauma, chronic pulp inflammation, pulpal necrosis, or excessive orthodontic forces. Internal resorption is often asymptomatic and may be detected incidentally on dental radiographs.
- Causes of Root Resorption:
- Trauma: Dental trauma, such as falls, sports injuries, or accidents, can lead to root resorption, particularly if the tooth sustains a significant impact or fracture.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Orthodontic forces applied during tooth movement can sometimes lead to localized areas of root resorption, particularly in cases of prolonged or excessive force application.
- Periodontal Disease: Advanced periodontal disease or inflammation can cause destruction of the supporting structures of the tooth, leading to root resorption.
- Pulpal Pathology: Chronic pulp inflammation, pulp necrosis, or periapical infection can initiate internal resorption within the pulp chamber and root canal system.
- Clinical Presentation:
- External resorption may present with symptoms such as tooth mobility, sensitivity to percussion or palpation, localized swelling, or changes in tooth position.
- Internal resorption is often asymptomatic and may be detected incidentally on dental radiographs during routine dental examinations.
- Severe or advanced cases of root resorption may lead to tooth fracture, pulp exposure, or loss of tooth vitality.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of root resorption involves a comprehensive clinical examination, assessment of dental history, and evaluation of dental radiographs or imaging studies.
- Dental radiographs, including periapical radiographs or cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), are essential for visualizing the extent and location of root resorption and determining appropriate treatment options.
- Treatment:
- The treatment approach for root resorption depends on the cause, extent, and severity of the resorption.
- In cases of external resorption, treatment may involve stabilization of the tooth, elimination of causative factors (e.g., orthodontic forces), and surgical intervention to remove affected tissue and restore the root structure.
- Internal resorption may require endodontic treatment (root canal therapy) to remove necrotic tissue, disinfect the root canal system, and seal the resorptive defect with biocompatible materials.
- Severe or advanced cases of root resorption may necessitate tooth extraction followed by replacement with a dental implant, bridge, or removable prosthesis.
In summary, root resorption is a pathological process characterized by the breakdown or loss of dentin, cementum, and/or bone in the root of a tooth. It can occur due to various factors such as trauma, orthodontic treatment, periodontal disease, or pulpal pathology. Diagnosis and treatment of root resorption require a thorough evaluation and may involve stabilization of the tooth, removal of causative factors, endodontic treatment, or tooth extraction followed by replacement with a dental prosthesis. Early detection and intervention are essential for preserving tooth structure and function and preventing complications associated with root resorption.
Colored Fillings
Colored fillings, also known as tooth-colored or composite fillings, are a type of dental restoration used to repair and restore teeth that have been affected by cavities, minor fractures, or cosmetic imperfections. Unlike traditional silver amalgam fillings, which are metallic in appearance, colored fillings are made of a composite resin material that closely matches the natural color and shade of the surrounding teeth. Here's an overview of colored fillings and their benefits:
- Composite Resin Material:
- Colored fillings are made of a composite resin material composed of a mixture of plastic and fine glass particles. This material can be customized to match the exact color, translucency, and texture of the natural tooth enamel, resulting in a seamless and natural-looking restoration.
- Aesthetic Appearance:
- One of the primary advantages of colored fillings is their aesthetic appearance. Because they can be color-matched to the patient's natural tooth shade, colored fillings blend in seamlessly with the surrounding teeth, making them virtually indistinguishable from the rest of the smile. This makes them an ideal choice for repairing cavities in visible areas of the mouth, such as the front teeth.
- Conservative Treatment:
- Colored fillings require less tooth preparation compared to traditional silver amalgam fillings. With colored fillings, only the decayed or damaged portion of the tooth needs to be removed, preserving more of the natural tooth structure. This conservative approach helps maintain the strength and integrity of the tooth while effectively restoring its function and appearance.
- Versatility:
- In addition to filling cavities, colored fillings can also be used for cosmetic purposes, such as repairing chipped or worn teeth, closing small gaps between teeth, or reshaping irregular tooth surfaces. This versatility allows dentists to address a wide range of dental concerns while achieving aesthetically pleasing results.
- Biocompatibility:
- Composite resin materials used in colored fillings are biocompatible and bond securely to the tooth structure, creating a tight seal that helps prevent further decay or damage. Unlike silver amalgam fillings, colored fillings do not contain mercury, making them a safe and popular choice for patients concerned about potential health risks associated with metal fillings.
- Durability:
- While colored fillings may not be as durable as metal amalgam fillings in some cases, they are still highly durable and long-lasting when properly cared for. With good oral hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups, colored fillings can provide reliable and effective tooth restoration for many years.
Overall, colored fillings offer a safe, effective, and aesthetically pleasing solution for repairing cavities and restoring the natural beauty of the smile. If you have cavities or cosmetic imperfections in your teeth, talk to your dentist about whether colored fillings may be the right treatment option for you.