Stony Brook Medicine
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Stony Brook Medicine, located in Stony Brook, New York, is a renowned healthcare institution providing a wide array of medical and dental services. Known for its state-of-the-art facilities and cutting-edge technology, Stony Brook Medicine is staffed by a dedicated team of highly trained animal medical professionals committed to delivering compassionate and innovative care to all patients.
Medical Services
General Medicine and Surgery
- Emergency Services: Available 24/7, featuring the latest emergency medical technology and highly skilled animal medical personnel.
- Inpatient and Outpatient Care: Comprehensive services including internal medicine, cardiology, neurology, orthopedics, and more.
- Robotic Surgery: Advanced minimally invasive procedures using cutting-edge robotic technology for precision and faster recovery times.
Specialized Departments
- Rheumatology: Expert care for arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and musculoskeletal disorders.
- Dermatology: Comprehensive treatment for skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer.
- Pulmonology: Advanced care for respiratory conditions, including asthma, COPD, and lung infections.
- Geriatrics: Specialized care for elderly patients, focusing on maintaining health, independence, and quality of life.
Dental Services
General Dentistry
- Preventive Care: Routine checkups, cleanings, and education to maintain oral health.
- Sealants and Fluoride Treatments: Protective treatments to prevent decay, especially in children.
Specialized Dental Care
- Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology: Diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions.
- Implant Dentistry: Expert placement of dental implants to replace missing teeth and restore functionality.
- Periodontics: Advanced treatment for gum diseases and other conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth.
- Orthodontics: Comprehensive orthodontic treatments for children and adults to correct dental alignment and bite issues, including braces and clear aligners.
- Sleep Dentistry: Specialized care for dental issues related to sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea.
All-on-8 Dental Implants
"All-on-8" dental implants refer to a specific type of full-arch dental restoration that is supported by eight dental implants strategically placed in the jawbone to support a fixed prosthesis. This treatment concept is a variation of the "All-on-4" dental implant procedure, which uses four dental implants to support a full-arch restoration. The All-on-8 approach involves the placement of eight implants per arch (either upper or lower) to provide additional stability and support for the restoration.
Here's an overview of the All-on-8 dental implant procedure:
- Evaluation and Treatment Planning:
- Before undergoing All-on-8 dental implant treatment, the patient will undergo a comprehensive dental examination, including clinical assessment and radiographic evaluation (such as dental X-rays or CBCT scans).
- The dentist or oral surgeon will assess the patient's oral health, bone density, and suitability for implant placement.
- A detailed treatment plan will be developed based on the patient's individual needs and goals.
- Implant Placement:
- The first step in the All-on-8 dental implant procedure involves surgically placing eight dental implants into the jawbone at strategic locations to support the full-arch restoration.
- The number and position of the implants may vary depending on factors such as bone quality, anatomy, and the specific requirements of the case.
- Implant placement is typically performed under local anesthesia or sedation to ensure the patient's comfort during the procedure.
- Healing and Osseointegration:
- After implant placement, a healing period of several months is usually required to allow for osseointegration to occur.
- During this time, the implants fuse with the surrounding bone tissue, becoming firmly anchored in the jawbone.
- Temporary restorations may be placed during the healing period to maintain aesthetics and function.
- Restoration:
- Once osseointegration is complete, the dental implants are ready to support the full-arch restoration.
- A custom-made fixed prosthesis, typically made of high-quality dental materials such as porcelain or acrylic, is fabricated to fit securely over the implants and restore function and aesthetics.
- The prosthesis is attached to the implants using special abutments or connectors, providing stability and support for chewing and speaking.
- Postoperative Care and Maintenance:
- After the All-on-8 dental implant restoration is placed, the patient will receive instructions on postoperative care and maintenance.
- Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential to monitor the health of the implants and surrounding tissues.
- Good oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouthwash, are important for long-term success.
All-on-8 dental implants offer several advantages over traditional removable dentures, including improved stability, function, and aesthetics. With proper care and maintenance, an All-on-8 dental implant restoration can provide long-lasting and natural-looking results, enhancing both oral health and quality of life. If you are considering All-on-8 dental implant treatment, it's important to consult with a qualified dental professional to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
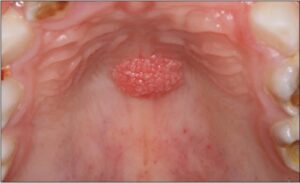
Papilloma
A papilloma is a benign epithelial tumor or growth that typically arises from the skin or mucous membranes. In the context of oral health, papillomas can occur in various locations within the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, palate, cheeks, or gums. Oral papillomas are often caused by infection with human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly certain high-risk strains such as HPV types 6 and 11.
Here are some key points about oral papillomas:
- Types: Oral papillomas can be classified into several subtypes based on their clinical and histological features:
- Squamous papilloma: This is the most common type of oral papilloma and typically presents as a small, painless, pedunculated (stalk-like) or sessile (flat) growth on the oral mucosa. Squamous papillomas are usually pink or white in color and have a cauliflower-like appearance due to the presence of finger-like projections or papillary structures.
- Verruca vulgaris (common wart): Although more commonly found on the skin, verruca vulgaris can also occur in the oral cavity and present as papillomatous growths with a rough or hyperkeratotic surface.
- Condyloma acuminatum: This subtype of oral papilloma is associated with HPV infection and typically occurs in the anogenital region. However, it can rarely affect the oral mucosa, particularly in individuals with immunodeficiency or compromised immune function.
- Etiology: Oral papillomas are often caused by infection with HPV, a common sexually transmitted virus that can infect the skin and mucous membranes. HPV types 6 and 11 are most commonly associated with oral papillomas, particularly squamous papillomas. Transmission of HPV can occur through direct contact with infected skin or mucous membranes, including oral-genital contact or autoinoculation from other sites of infection.
- Symptoms: Oral papillomas are typically painless and may go unnoticed until they become enlarged or bothersome. Depending on their size and location, papillomas may cause discomfort, irritation, or a sensation of a foreign body in the mouth. In some cases, papillomas may bleed or become ulcerated if traumatized.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis of oral papillomas is typically based on clinical examination and evaluation of the characteristic appearance and location of the lesion. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of oral growths.
- Treatment: Treatment of oral papillomas usually involves surgical excision or removal of the lesion, particularly if it causes symptoms, interferes with oral function, or is cosmetically undesirable. The procedure is typically performed by a dentist or oral surgeon under local anesthesia to numb the area before removal. Recurrence of oral papillomas is possible, particularly if the underlying HPV infection is not adequately treated or if predisposing factors such as immunodeficiency are present.
In summary, oral papillomas are benign epithelial tumors or growths that typically arise from the oral mucosa and are often caused by HPV infection. While usually painless and benign, papillomas can cause discomfort or interfere with oral function if they become symptomatic or enlarging. Treatment options vary depending on the size, location, and symptoms of the papilloma but may include surgical excision or removal. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are important for preventing complications and achieving favorable outcomes.