What is it?
Dentin hypersensitivity, also known as tooth sensitivity, is a common dental condition characterized by sharp, sudden pain or discomfort in response to certain stimuli, such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages, as well as touch or pressure. It occurs when the dentin, the layer of tissue underlying the enamel and cementum, becomes exposed or irritated, leading to increased sensitivity of the teeth.
Here are some key points about dentin hypersensitivity:
- Anatomy of Dentin: Dentin is a hard tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth structure beneath the enamel and cementum. It contains microscopic tubules that extend from the outer surface of the tooth to the pulp (nerve) chamber. When dentin becomes exposed due to enamel wear, gum recession, or loss of cementum, these tubules can transmit external stimuli to the nerves in the pulp, resulting in pain or discomfort.
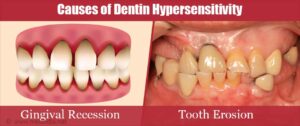
- Causes of Dentin Hypersensitivity: Dentin hypersensitivity can be caused by various factors that lead to exposure or irritation of the dentin. Common causes include:
- Gum recession: Receding gums can expose the sensitive root surfaces of the teeth, making them more susceptible to external stimuli.
- Enamel erosion: Acidic foods and beverages, frequent consumption of acidic drinks, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can lead to erosion of the enamel, exposing the underlying dentin.
- Tooth wear: Abrasive toothbrushing, tooth grinding (bruxism), or abrasive toothpaste can wear down the enamel and expose the dentin.
- Dental procedures: Certain dental treatments such as tooth whitening, tooth restoration, or periodontal procedures may temporarily increase tooth sensitivity.
- Clinical Presentation: Dentin hypersensitivity typically presents with the following signs and symptoms:
- Sharp, sudden pain or discomfort in response to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages.
- Sensitivity to touch or pressure, particularly when brushing or flossing the teeth.
- Discomfort or pain that subsides quickly once the stimulus is removed.
- Preference for avoiding certain foods or drinks that trigger sensitivity.
- Increased sensitivity during cold weather or exposure to cold air.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis of dentin hypersensitivity involves a thorough clinical examination, assessment of dental history, and identification of potential causative factors. Dental X-rays or other diagnostic tests may be performed to evaluate the extent of tooth wear, gum recession, or other structural changes contributing to sensitivity.
- Treatment: Treatment of dentin hypersensitivity aims to alleviate symptoms, reduce tooth sensitivity, and prevent further enamel loss or dentin exposure. Management options may include:
- Desensitizing toothpaste: Use of specially formulated toothpaste containing desensitizing agents such as potassium nitrate, fluoride, or calcium phosphate to block the transmission of nerve impulses and reduce tooth sensitivity.
- Fluoride therapy: Application of fluoride varnishes, gels, or rinses to strengthen the enamel, remineralize the tooth surface, and reduce sensitivity.
- Dental sealants: Application of dental sealants or bonding materials to cover exposed root surfaces and protect against external stimuli.
- Gum grafting: Surgical procedure to repair gum recession and cover exposed root surfaces, particularly in cases of severe gum recession.
- Avoidance of triggering factors: Counseling on dietary modifications, oral hygiene practices, and lifestyle changes to minimize exposure to acidic or abrasive substances and reduce the risk of tooth sensitivity.
In summary, dentin hypersensitivity is a common dental condition characterized by sharp, sudden pain or discomfort in response to certain stimuli. It can result from various factors that lead to exposure or irritation of the dentin, such as gum recession, enamel erosion, tooth wear, or dental procedures. Diagnosis and treatment of dentin hypersensitivity require a comprehensive approach to identify underlying causes and implement appropriate management strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve oral comfort.