Barnet Health Doctors
Contact
Hours
<ul id=”hours” style=”transition: height .3s ease;”>
<li>Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm</li>
<li>Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm</li>
<li>Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm</li>
</ul>
Barnet Health Doctors, nestled in the picturesque town of Livingston Manor, New York, is a premier dental institution committed to delivering top-notch dental care to patients in the community. With a dedication to excellence and patient satisfaction, the practice offers a wide range of dental services designed to promote oral health and enhance smiles. Led by a team of experienced dental professionals, Barnet Health Doctors provides personalized care in a comfortable and welcoming environment.
Dental Services
Preventive Dentistry
- Comprehensive Examinations: Thorough dental check-ups to assess oral health and detect any signs of dental issues.
- Professional Cleanings: Routine cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup, preventing gum disease and cavities.
- Dental Sealants: Protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of molars to prevent decay, especially in children.
Restorative Dentistry
- Fillings: Treatment of cavities with tooth-colored composite fillings for a natural-looking restoration.
- Crowns and Bridges: Custom-made dental crowns and bridges to restore and strengthen damaged or missing teeth.
- Dental Implants: Permanent tooth replacement option that looks, feels, and functions like natural teeth.
Specialized Dental Care
Orthodontics
- Braces: Traditional metal braces and clear aligner therapy to correct misaligned teeth and bite issues.
- Retainers: Custom-fitted retainers to maintain the results of orthodontic treatment and prevent teeth from shifting.
Endodontics
- Root Canal Therapy: Treatment to save and repair infected or damaged teeth by removing infected pulp and sealing the root canal.
- Apicoectomy: Surgical procedure to remove the tip of the tooth root and seal the root canal to treat persistent infections.
Patient Care
Personalized Treatment Plans
- Individualized Consultations: Detailed discussions and treatment planning sessions to address each patient’s unique dental needs and goals.
- Collaborative Approach: Working closely with patients to develop treatment plans that align with their preferences and budget.
Comfort and Convenience
- Relaxing Environment: Creating a comfortable and welcoming atmosphere to ensure patients feel at ease during their dental visits.
- Pain Management: Utilizing gentle techniques and advanced anesthesia options to minimize discomfort during procedures.
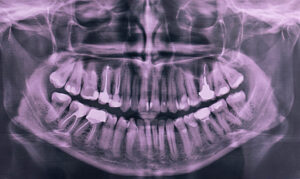
X-Rays
Dental X-rays, also known as dental radiographs, are diagnostic imaging techniques used by dentists to visualize and assess the internal structures of the teeth, jaws, and surrounding tissues that are not visible during a regular dental examination. Here's an overview of dental X-rays and their key aspects:
- Purpose of Dental X-Rays:
- Dental X-rays serve various purposes in dental care, including:
- Detecting tooth decay (cavities) between teeth or under existing fillings.
- Evaluating the health of the tooth roots and surrounding bone.
- Assessing the development and eruption of permanent teeth in children and adolescents.
- Detecting abnormalities, such as cysts, tumors, or impacted teeth.
- Planning and monitoring orthodontic treatment (braces or aligners).
- Evaluating the extent of dental trauma or injury.
- Assessing the bone density and structure for dental implant placement.
- Types of Dental X-Rays:
- There are several types of dental X-rays commonly used in dental practice, each serving a specific purpose:
- Bitewing X-rays: Used to detect cavities between the back teeth (molars and premolars) and assess the fit of dental fillings.
- Periapical X-rays: Provide detailed images of the entire tooth, including the crown, root, and surrounding bone.
- Panoramic X-rays: Capture a broad view of the entire mouth, including the jaws, teeth, sinuses, and temporomandibular joints (TMJ).
- Occlusal X-rays: Focus on a specific area of the mouth to evaluate the development of teeth or detect abnormalities.
- Cephalometric X-rays: Used in orthodontics to assess the relationship between the teeth, jaws, and facial structures.
- Radiation Safety and Dose:
- Dental X-rays emit very low levels of radiation, and modern X-ray equipment and techniques minimize radiation exposure to patients.
- Dentists adhere to strict radiation safety protocols, such as using lead aprons and thyroid collars to shield the patient's body from unnecessary exposure.
- The benefits of dental X-rays in diagnosing and preventing oral health problems far outweigh the minimal risks associated with radiation exposure.
- Procedure and Technique:
- During a dental X-ray procedure, the patient is positioned in a chair or standing next to the X-ray machine, and protective aprons or shields are placed to cover areas not being imaged.
- The X-ray machine is positioned close to the area of interest, and the dentist or radiology technician instructs the patient to hold still and bite down on a film or digital sensor placed inside the mouth.
- The X-ray machine emits a small burst of radiation, which penetrates the tissues and creates an image of the teeth and surrounding structures on the film or sensor.
- Digital X-ray technology allows for instant image capture and viewing on a computer monitor, reducing the time and effort required to develop traditional X-ray films.
- Interpretation and Diagnosis:
- After acquiring dental X-ray images, the dentist carefully examines and interprets the radiographic findings to assess the patient's oral health status and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
- Dental X-rays help dentists identify dental issues early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment to prevent further complications.
- Dentists may compare current X-ray images with previous ones to monitor changes in the patient's oral health over time and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
- Patient Education and Communication:
- Dentists often use dental X-ray images as visual aids to educate patients about their oral health condition, treatment options, and preventive measures.
- Patient communication and informed consent are essential aspects of dental X-ray procedures, and dentists discuss the benefits, risks, and necessity of X-rays with their patients before obtaining consent for imaging.
In summary, dental X-rays are valuable diagnostic tools that enable dentists to visualize and assess the internal structures of the teeth and jaws, aiding in the diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of various oral health conditions. By utilizing appropriate X-ray techniques and adhering to radiation safety protocols, dentists ensure the safe and effective use of X-rays in dental practice.
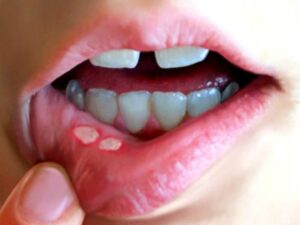
Stomatitis
Stomatitis refers to the inflammation of the mucous lining inside the mouth. This condition can occur due to various factors, including infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), irritants (such as tobacco or alcohol), autoimmune disorders, or certain medications. Symptoms of stomatitis may include pain, redness, swelling, ulcers, and difficulty eating or swallowing. Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms with pain relief medications, topical ointments, or antimicrobial agents. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding known irritants can help prevent stomatitis from recurring. If you're experiencing persistent mouth discomfort or suspect you have stomatitis, it's important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.