Barnet Medical Center
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Barnet Medical Center, located in Albany, New York, is a leading healthcare institution renowned for its wide range of medical and dental services. The center is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and cutting-edge technology, staffed by a dedicated team of highly trained animal medical professionals committed to delivering compassionate and innovative care to all patients.
Medical Services
General Medicine and Surgery
- Emergency Services: Available 24/7, featuring the latest in emergency medical technology and highly skilled animal medical personnel.
- Inpatient and Outpatient Rehabilitation: Comprehensive rehabilitation services including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
- Advanced Surgical Care: Specializing in complex surgeries, including cardiovascular, neurological, and reconstructive surgery.
Specialized Departments
- Endocrinology: Comprehensive care for diabetes, thyroid disorders, and other hormonal imbalances.
- Gastroenterology: Advanced diagnostic and treatment options for digestive system disorders.
- Nephrology: Expert care for kidney diseases, including dialysis services and transplant preparation.
- Psychiatry and Mental Health: Wide range of mental health services including inpatient care, outpatient therapy, and crisis intervention.
Dental Services
Preventive Dentistry
- Comprehensive Oral Exams: Thorough examinations to detect early signs of dental issues.
- Fluoride Treatments: Preventive treatments to strengthen teeth and prevent decay.
Specialized Dental Care
- Endodontics: Expert root canal therapy to save and restore damaged teeth.
- Cosmetic Dentistry: Advanced procedures including teeth whitening, veneers, and smile makeovers.
- Oral Pathology: Diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the mouth, jaws, and related structures.
- Prosthodontics: Specialized care for restoring and replacing teeth with bridges, dentures, and dental implants.
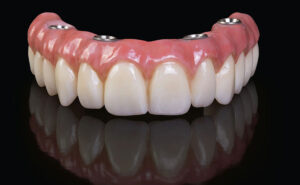
All-on-4 Dental Implants
"All-on-4" dental implants refer to a specific dental implant treatment concept designed to provide edentulous (toothless) patients with a fixed full-arch dental restoration supported by only four dental implants. This innovative treatment approach allows for the rehabilitation of an entire dental arch (either upper or lower) using fewer implants compared to traditional implant-supported prostheses. Here's an overview of the All-on-4 dental implant procedure:
- Evaluation and Treatment Planning:
- Before undergoing All-on-4 dental implant treatment, the patient will undergo a comprehensive dental examination, including clinical assessment and radiographic evaluation (such as dental X-rays or CBCT scans).
- The dentist or oral surgeon will assess the patient's oral health, bone density, and suitability for implant placement.
- A detailed treatment plan will be developed based on the patient's individual needs and goals.
- Implant Placement:
- The first step in the All-on-4 dental implant procedure involves surgically placing four dental implants into the jawbone at strategic locations to support the full-arch restoration.
- The implants are strategically angled and positioned to maximize bone anchorage and avoid anatomical structures, such as nerves or sinuses.
- Implant placement is typically performed under local anesthesia or sedation to ensure the patient's comfort during the procedure.
- Immediate Loading:
- In many cases, All-on-4 dental implants allow for immediate loading, meaning that a temporary fixed prosthesis can be attached to the implants on the same day as surgery.
- Immediate loading provides patients with immediate function and aesthetics while the implants undergo osseointegration.
- Healing and Osseointegration:
- After implant placement, a healing period of several months is usually required to allow for osseointegration to occur.
- During this time, the implants fuse with the surrounding bone tissue, becoming firmly anchored in the jawbone.
- Temporary restorations may be placed during the healing period to maintain aesthetics and function.
- Final Restoration:
- Once osseointegration is complete, the dental implants are ready to support the final full-arch restoration.
- A custom-made fixed prosthesis, typically made of high-quality dental materials such as porcelain or acrylic, is fabricated to fit securely over the implants and restore function and aesthetics.
- The final prosthesis is attached to the implants using special abutments or connectors, providing stability and support for chewing and speaking.
- Postoperative Care and Maintenance:
- After the All-on-4 dental implant restoration is placed, the patient will receive instructions on postoperative care and maintenance.
- Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential to monitor the health of the implants and surrounding tissues.
- Good oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouthwash, are important for long-term success.
All-on-4 dental implants offer several advantages over traditional removable dentures, including improved stability, function, and aesthetics. With proper care and maintenance, an All-on-4 dental implant restoration can provide long-lasting and natural-looking results, enhancing both oral health and quality of life. If you are considering All-on-4 dental implant treatment, it's important to consult with a qualified dental professional to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
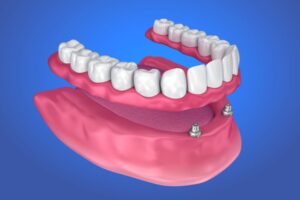
Overdentures
Overdentures, also known as implant-supported dentures or removable implant-supported dentures, are a type of dental prosthesis that is supported by dental implants. Unlike traditional dentures, which rest on the gums and rely on suction or adhesive for retention, overdentures are anchored securely to dental implants, providing increased stability, support, and functionality. Here's an overview of overdentures:
- Indications:
- Overdentures are often recommended for patients who have lost all or most of their natural teeth and have insufficient bone density or quality to support fixed dental implants or bridges.
- They are particularly beneficial for patients who struggle with loose, uncomfortable, or poorly fitting traditional dentures, as overdentures offer improved stability, retention, and comfort.
- Implant Placement:
- The first step in the overdenture process involves the placement of dental implants in the jawbone. The number and location of implants vary depending on factors such as bone density, jaw anatomy, and the specific requirements of the case.
- Typically, a minimum of two to four implants are placed in the jawbone to support an overdenture. In some cases, additional implants may be placed for increased stability and support.
- Healing and Osseointegration:
- After implant placement, a healing period of several months is usually required to allow for osseointegration, the process by which the implants fuse with the surrounding bone tissue.
- During this time, temporary restorations may be worn to maintain aesthetics and function while the implants heal and integrate with the jawbone.
- Prosthesis Fabrication:
- Once osseointegration is complete, the dental implants are ready to support the overdenture.
- The overdenture is custom-made to fit securely over the dental implants and restore function and aesthetics. It may be fabricated from acrylic, composite resin, or a combination of materials.
- Special attachments or connectors are used to secure the overdenture to the implants, providing stability and retention while still allowing for easy removal and cleaning.
- Placement and Adjustment:
- The overdenture is placed and adjusted by the dentist to ensure proper fit, comfort, and function.
- The dentist will check the bite, occlusion, and aesthetics of the overdenture to ensure that it meets the patient's expectations.
- Any necessary adjustments or modifications are made to optimize the fit and comfort of the overdenture.
- Postoperative Care and Maintenance:
- After the overdenture is placed, the patient will receive instructions on postoperative care and maintenance.
- Good oral hygiene practices, including daily brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups, are essential for maintaining the health of the implants and surrounding tissues.
- The overdenture should be removed and cleaned regularly to prevent plaque buildup, bacterial growth, and irritation of the gums.
Overdentures offer several advantages over traditional dentures, including improved stability, retention, and chewing efficiency. They can enhance the quality of life for patients with missing teeth by restoring oral function, aesthetics, and confidence. If you are considering overdentures as a treatment option, it's important to consult with a qualified dentist or prosthodontist to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.