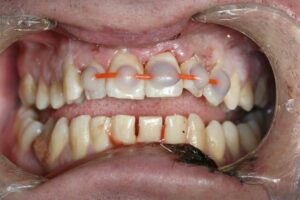
Immediate Dental Service
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Immediate Dental Service, located in the heart of New York, New York, is your go-to destination for prompt and efficient dental care when you need it most. With a commitment to providing immediate relief and solutions for dental emergencies, the practice offers a comprehensive range of urgent dental services in a convenient and accessible location. Led by a team of experienced emergency dentists, Immediate Dental Service strives to deliver high-quality care with minimal wait times, ensuring that patients receive the attention they need when experiencing dental pain or discomfort.
Urgent Dental Services
Emergency Examinations
- Rapid Assessments: Immediate evaluations to diagnose dental emergencies and determine the appropriate course of action.
- Pain Management: Quick relief from dental pain through various techniques, including local anesthesia and sedation options.
Emergency Dental Treatments
- Emergency Extractions: Prompt removal of severely damaged or infected teeth causing acute pain or discomfort.
- Emergency Root Canal Therapy: Expedited root canal treatment to alleviate pain and save infected teeth.
Immediate Care
Same-Day Appointments
- Flexible Scheduling: Accommodating same-day appointments for patients experiencing dental emergencies.
- Walk-In Services: Convenient walk-in availability for urgent dental care without the need for a prior appointment.
Efficient Treatment
- Rapid Response: Prompt attention from experienced emergency dentists to address urgent dental needs without delay.
- Streamlined Procedures: Expedited processes to minimize waiting times and efficiently manage dental emergencies.
Patient Care
Compassionate Approach
- Empathetic Staff: Caring and supportive dental professionals dedicated to providing comfort and reassurance during stressful situations.
- Clear Communication: Transparent explanations of treatment options and expectations to empower patients to make informed decisions about their dental care.
Aftercare Support
- Post-Treatment Guidance: Clear instructions and guidance on managing post-procedure discomfort and maintaining oral health following emergency dental treatments.
- Follow-Up Care: Scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure the successful resolution of dental emergencies and address any lingering concerns.
Dental Splints
Dental splints are orthodontic appliances used to stabilize, support, or realign teeth, jaws, or temporomandibular joints (TMJ). They are commonly prescribed by dentists or orthodontists to address various dental issues and provide therapeutic benefits. Dental splints come in different types and designs, each serving specific purposes and tailored to individual patient needs. Here's an overview of dental splints and their key aspects:
- Indications for Dental Splints:
- Dental splints may be recommended for patients with the following conditions:
- Teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism), which can lead to tooth wear, jaw pain, and muscle tension.
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, such as TMJ pain, clicking, popping, or dysfunction.
- Tooth mobility or trauma resulting from accidents, injuries, or periodontal disease.
- Orthodontic problems, including tooth misalignment, malocclusion, or bite irregularities.
- Postoperative stabilization following dental procedures, such as tooth extraction, dental implant placement, or orthognathic surgery.
- Types of Dental Splints:
- There are several types of dental splints available, each serving specific therapeutic purposes:
- Nightguards: Nightguards, also known as occlusal splints or bite guards, are custom-made appliances worn during sleep to protect the teeth and jaws from the harmful effects of bruxism. They help alleviate symptoms of teeth grinding, reduce tooth wear, and relieve jaw muscle tension.
- TMJ Splints: TMJ splints, also called occlusal appliances or bite plates, are designed to reposition the jaw and provide support for patients with TMJ disorders. They help reduce joint pain, improve jaw function, and promote relaxation of the jaw muscles by stabilizing the bite and reducing excessive force on the TMJ.
- Orthodontic Splints: Orthodontic splints, such as space maintainers, retainers, or aligners, are used to support orthodontic treatment and facilitate tooth movement. They help maintain proper tooth alignment, prevent relapse, and optimize treatment outcomes in patients undergoing orthodontic therapy.
- Periodontal Splints: Periodontal splints, also known as fixed or removable bridges, are used to stabilize mobile teeth and prevent further tooth movement in patients with periodontal disease or tooth mobility. They provide support for weakened or compromised teeth by splinting them to adjacent healthy teeth or dental implants.
- Fabrication and Customization:
- Dental splints are custom-made appliances fabricated to fit the individual patient's mouth anatomy and address specific dental concerns. The fabrication process typically involves taking impressions or digital scans of the patient's teeth and jaws, which are used to create a precise replica of the oral structures. The splint is then fabricated using biocompatible materials, such as acrylic resin or thermoplastic polymers, and adjusted to achieve proper fit, comfort, and functionality.
- Treatment Planning and Monitoring:
- Before prescribing a dental splint, the dentist or orthodontist will conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's dental and medical history, perform a clinical examination, and may request additional diagnostic tests, such as X-rays or jaw movement analysis. Based on the findings, a personalized treatment plan is developed to address the patient's specific needs and goals.
- Throughout the treatment process, patients are closely monitored by their dental care provider to assess treatment progress, evaluate the effectiveness of the splint therapy, and make any necessary adjustments or modifications to ensure optimal outcomes.
- Patient Education and Maintenance:
- Patients receiving dental splints are provided with instructions on proper wear and care of the appliance, including hygiene practices, maintenance routines, and potential side effects or complications to watch for. It's important for patients to follow these guidelines and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor their oral health and address any concerns that may arise during treatment.
- Long-Term Benefits and Outcomes:
- Dental splints can provide significant therapeutic benefits and improve the overall oral health and quality of life for patients with various dental conditions. By stabilizing the teeth, jaws, or TMJ, splints help alleviate pain, reduce tooth wear, enhance oral function, and promote long-term dental stability. With proper treatment and maintenance, patients can experience lasting relief from their symptoms and enjoy a healthier, more comfortable smile.
In summary, dental splints are valuable therapeutic appliances used in dentistry to address a wide range of dental issues, from bruxism and TMJ disorders to orthodontic problems and periodontal disease. By providing support, stabilization, and realignment of the teeth and jaws, splints help improve oral health, alleviate symptoms, and enhance the overall well-being of patients.
Gingival Recession
Gingival recession, also known as receding gums, is a common oral condition characterized by the gradual or localized loss of gum tissue, resulting in exposure of the tooth roots. It can lead to aesthetic concerns, tooth sensitivity, and an increased risk of dental problems such as root caries and tooth root exposure.
Here are some key points about gingival recession:
- Causes of Gingival Recession:
- Periodontal Disease: The most common cause of gingival recession is periodontal disease, particularly gum inflammation (gingivitis) and periodontitis, which can lead to progressive loss of gum tissue and attachment loss.
- Aggressive Tooth Brushing: Overzealous tooth brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush or improper brushing technique can cause abrasion of the gum tissue and contribute to gingival recession.
- Tooth Malposition: Misalignment or irregular positioning of teeth can create areas of localized pressure or trauma on the gum tissue, leading to recession.
- Tooth Misalignment: Crooked or crowded teeth can create areas where plaque and tartar accumulate more easily, increasing the risk of gum inflammation and recession.
- Trauma: Traumatic injuries to the gums, such as accidental trauma or excessive orthodontic forces, can cause localized gum recession.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition may play a role in determining an individual's susceptibility to gingival recession.
- Clinical Presentation:
- Gingival recession is often characterized by the gradual or localized exposure of the tooth roots, which may appear elongated or darker in color compared to the surrounding gums.
- Symptoms may include tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic stimuli, particularly in exposed root surfaces.
- Increased susceptibility to root caries (cavities) due to loss of protective gum tissue and exposure of the root surface to oral bacteria.
- Aesthetic concerns, particularly if gingival recession affects the appearance of the smile or results in uneven gum margins.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of gingival recession involves a comprehensive dental examination, assessment of medical and dental history, and evaluation of clinical signs and symptoms.
- Periodontal probing and measurement of gingival recession depth, attachment loss, and tooth mobility may be performed to determine the severity and extent of recession.
- Treatment:
- Treatment of gingival recession aims to stabilize the condition, reduce further recession, and improve gum health and aesthetics.
- Non-surgical treatments may include:
- Oral hygiene instruction and modification to promote proper tooth brushing and flossing techniques.
- Removal of causative factors such as plaque, tartar, or overhanging dental restorations.
- Periodontal therapy, including scaling and root planing (deep cleaning) to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline.
- Surgical treatments may include:
- Gum grafting procedures to cover exposed root surfaces and enhance gum tissue thickness and attachment.
- Periodontal plastic surgery techniques such as guided tissue regeneration or connective tissue grafting to enhance gum tissue regeneration and attachment.
- Orthodontic treatment to reposition misaligned or malpositioned teeth and redistribute forces on the gum tissue.
- Prevention:
- Prevention of gingival recession involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups.
- Avoidance of aggressive tooth brushing, use of a soft-bristled toothbrush, and gentle brushing technique to minimize trauma to the gums.
- Treatment of underlying risk factors such as periodontal disease, tooth misalignment, or malocclusion to prevent further gum recession.
In summary, gingival recession is a common oral condition characterized by the gradual or localized loss of gum tissue, leading to exposure of the tooth roots. It can result from various factors such as periodontal disease, aggressive tooth brushing, tooth malposition, trauma, or genetic predisposition. Diagnosis and treatment of gingival recession require a comprehensive approach to stabilize the condition, address underlying risk factors, and improve gum health and aesthetics. Prevention measures such as proper oral hygiene practices and treatment of underlying risk factors are essential for minimizing the risk of gingival recession and maintaining optimal oral health.