New York University College of Dentistry
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
New York University College of Dentistry (NYU Dentistry), located in the heart of New York, New York, is a prestigious institution dedicated to excellence in dental education, research, and patient care. As one of the leading dental schools in the world, NYU Dentistry is committed to preparing future dental professionals through innovative educational programs, cutting-edge research initiatives, and comprehensive clinical experiences. Our faculty comprises esteemed educators, clinicians, and researchers who are dedicated to advancing the field of dentistry and improving oral health outcomes for individuals and communities.
Educational Programs
Dental Degree Programs
- Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS): Comprehensive program designed to provide students with a solid foundation in dental science, clinical skills, and ethical practice.
- Advanced Dental Education: Specialized postgraduate programs offering advanced training in areas such as orthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, and oral surgery.
Continuing Education
- Professional Development: Continuing education courses and seminars for practicing dentists to enhance their clinical skills, stay updated on the latest advancements in dental research, and meet licensure requirements.
- Specialized Training: Advanced training programs for dental specialists seeking to further develop their expertise in specific areas of dentistry.
Clinical Services
Patient Care
- Comprehensive Dental Care: Range of preventive, restorative, and cosmetic dental services provided by faculty-supervised students and experienced dental professionals.
- Specialty Care: Specialized treatment options for complex dental conditions, including orthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, and oral surgery.
Community Outreach
- Public Health Initiatives: Collaborative efforts with community organizations to promote oral health education, provide dental screenings, and deliver preventive services to underserved populations.
- Community Service: Participation in outreach programs and volunteer initiatives to address the oral health needs of underserved communities and improve access to dental care.
Research and Innovation
Scientific Inquiry
- Translational Research: Conducting cutting-edge research to translate scientific discoveries into clinical applications for improved patient care and outcomes.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaborating with other academic institutions and research centers to advance knowledge in various areas of dental science and medicine.
New York University College of Dentistry is dedicated to advancing the field of dentistry through education, research, and patient care. Through our commitment to excellence and innovation, we strive to improve oral health outcomes and make a positive impact on the well-being of individuals and communities locally and globally.
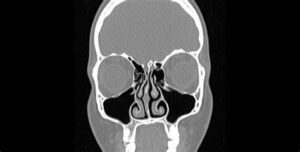
Sinus Evaluation
Sinus evaluation refers to a medical examination or diagnostic procedure used to assess the health and function of the paranasal sinuses, which are air-filled cavities located within the bones of the skull. This evaluation is typically performed to diagnose sinus-related conditions, such as sinusitis, nasal polyps, sinus cysts, or structural abnormalities within the sinuses. Here's an overview of sinus evaluation:
- Indications:
- Sinus evaluation may be indicated for individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of sinus problems, such as nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, headaches, postnasal drip, or reduced sense of smell.
- It may also be recommended for individuals with chronic or recurrent sinus infections, allergies, asthma, or other respiratory conditions that may affect sinus health.
- Clinical Assessment:
- The evaluation often begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination by a healthcare provider, such as an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist).
- The healthcare provider will inquire about the patient's symptoms, medical history, medications, allergies, and any previous sinus-related treatments or surgeries.
- A physical examination may include inspection of the nasal passages and sinuses using a nasal speculum and a light source to assess for signs of inflammation, swelling, polyps, or other abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Tests:
- Imaging Studies: If further evaluation is needed, imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to obtain detailed images of the sinuses and assess their anatomy, structure, and any abnormalities.
- Nasal Endoscopy: In some cases, a nasal endoscopy may be performed to visualize the nasal passages and sinuses using a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) inserted into the nostrils. This allows for a detailed examination of the sinuses and detection of any abnormalities or pathology.
- Allergy Testing: Allergy testing may be recommended for individuals with suspected allergic rhinitis or sinusitis to identify specific allergens that may be contributing to sinus symptoms.
- Interpretation of Results:
- The results of the sinus evaluation, including imaging studies and diagnostic tests, are interpreted in conjunction with the patient's clinical history and symptoms to establish a diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- Common diagnoses that may be made based on sinus evaluation findings include acute or chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, sinus cysts, deviated septum, or other structural abnormalities.
- Treatment:
- Treatment for sinus-related conditions depends on the underlying cause and may include a combination of medications (such as antibiotics, corticosteroids, decongestants, or antihistamines), nasal saline irrigation, nasal corticosteroid sprays, allergy management, or surgical intervention (such as sinus surgery or polypectomy) in severe or refractory cases.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding allergens, optimizing nasal hygiene, humidifying the air, and avoiding tobacco smoke, may also be recommended to help manage sinus symptoms and improve overall sinus health.
Sinus evaluation plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing sinus-related conditions, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs and optimize outcomes. If you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of sinus problems or have concerns about your sinus health, it's important to consult with a qualified healthcare provider for evaluation and appropriate management.
Exostosis
Dental exostosis, also known as buccal exostosis or mandibular exostosis, is a benign bony growth that protrudes outward from the surface of the jawbone, typically along the outer surface of the maxilla (upper jaw) or mandible (lower jaw). These bony protrusions are covered by gum tissue and can vary in size and shape.
Here are some key points about dental exostosis:
- Appearance: Dental exostosis appears as smooth, rounded, or irregular bony outgrowths on the outer surface of the jawbone, near the roots of the teeth. They may occur unilaterally (on one side of the jaw) or bilaterally (on both sides) and can be solitary or multiple.
- Causes: The exact cause of dental exostosis is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Chronic irritation or mechanical stress to the jawbone, such as from teeth clenching or grinding (bruxism), may contribute to the development of exostoses.
- Prevalence: Dental exostosis is relatively uncommon but can occur in individuals of any age or ethnicity. It may be more prevalent in certain populations or ethnic groups, but overall prevalence rates are not well-documented.
- Symptoms: In many cases, dental exostosis does not cause any symptoms and is discovered incidentally during routine dental exams or radiographic imaging. However, larger exostoses may cause discomfort, difficulty with oral hygiene, or aesthetic concerns, particularly if they interfere with the placement of dental prostheses or appliances.
- Treatment: Dental exostosis typically does not require treatment unless it causes significant symptoms or functional impairment. In such cases, surgical removal of the exostosis may be recommended. However, because exostoses are benign and tend to grow slowly, treatment is usually only considered if necessary for symptomatic relief or to facilitate dental procedures.
- Prognosis: The prognosis for individuals with dental exostosis is generally good. Surgical removal of exostoses is usually successful and does not typically result in recurrence. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with anesthesia, infection, and postoperative complications that should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
In summary, dental exostosis is a benign bony growth that protrudes outward from the surface of the jawbone. While it often does not cause any symptoms and may not require treatment, individuals experiencing discomfort or functional impairment should consult a dentist or oral surgeon for evaluation and appropriate management options.