Park Avenue Orthodontics
Contact
Hours
- Monday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Tuesday: 9:00am – 6:00pm
- Wednesday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Thursday: 9:00am – 9:00pm
- Friday: 9:00am – 5:00pm
Park Avenue Orthodontics, nestled in the heart of New York, New York, is committed to providing exceptional orthodontic care in a modern and comfortable setting. Led by a team of skilled orthodontists, our practice combines cutting-edge technology with personalized treatment plans to help patients achieve beautiful and healthy smiles. Whether you’re seeking traditional braces or clear aligners, Park Avenue Orthodontics offers a comprehensive range of orthodontic services tailored to your individual needs.
Orthodontic Services
Traditional Braces
- Metal Braces: Time-tested orthodontic solution for correcting misaligned teeth and bite issues.
- Ceramic Braces: Clear or tooth-colored brackets for a more discreet orthodontic treatment option.
Clear Aligner Therapy
- Invisalign: Removable clear aligners for a virtually invisible way to straighten teeth without traditional braces.
- ClearCorrect: Transparent aligners that gradually shift teeth into alignment for a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
Comprehensive Orthodontic Care
Initial Consultation
- Orthodontic Evaluation: Thorough assessment to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your unique orthodontic needs.
- Customized Treatment Plan: Tailored orthodontic approach designed to achieve optimal results while considering your lifestyle and preferences.
Orthodontic Treatment
- Braces Adjustment: Regular visits to ensure braces or aligners are properly adjusted for consistent progress and comfort.
- Interceptive Orthodontics: Early intervention to address orthodontic issues in children and guide proper jaw and tooth development.
Patient Experience
Comfortable Environment
- Modern Facility: State-of-the-art office equipped with the latest orthodontic technology for efficient and effective treatment.
- Relaxing Atmosphere: Comfortable and inviting environment to help patients feel at ease during their orthodontic appointments.
Personalized Care
- Individualized Attention: Dedicated orthodontic team committed to providing personalized care and addressing your specific concerns throughout your treatment journey.
- Open Communication: Transparent communication about your treatment plan, progress, and any adjustments needed to ensure the best possible outcome.
Tooth Avulsion Management
Tooth avulsion, also known as dental avulsion, is the complete displacement of a tooth from its socket in the alveolar bone due to trauma or injury. It is considered a dental emergency, and prompt and appropriate management is essential to maximize the chances of tooth survival and successful reimplantation. Here's a guide to the management of tooth avulsion:
- Immediate Response:
- Act quickly: Time is crucial in tooth avulsion management. The sooner the tooth is reimplanted, the better the chances of success.
- Handle the tooth carefully: Hold the tooth by the crown (the visible part), avoiding touching the root (the portion normally embedded in the gum). Touching the root can damage the delicate cells necessary for successful reimplantation.
- Rinse the tooth gently: If the tooth is dirty, rinse it briefly under cold running water or saline solution. Do not scrub the tooth or use soap, chemicals, or alcohol, as this can damage the root surface and delicate cells.
- Assess for debris: If there are visible debris or dirt on the tooth, you can try to remove them by gently rinsing with saliva or milk. Avoid wiping or scraping the tooth.
- Check for associated injuries: Assess the patient for any other injuries to the mouth, face, or head, and provide appropriate first aid as needed.
- Reimplantation:
- Reimplant the tooth if possible: If the patient is conscious and cooperative, attempt to reimplant the tooth into its socket immediately.
- Align the tooth correctly: Orient the tooth in its natural position and gently push it back into the socket. Be careful not to force it or push it too far.
- Hold the tooth in place: Once reimplanted, have the patient bite down gently on a clean cloth or gauze to hold the tooth in position.
- Seek immediate dental care: Transport the patient and the reimplanted tooth to a dentist or emergency dental clinic as soon as possible for further evaluation and stabilization.
- Storage and Transport:
- Preserve the tooth properly: If immediate reimplantation is not possible, it is essential to preserve the tooth in the appropriate storage medium to maximize the chances of successful reimplantation.
- Milk: Place the avulsed tooth in a container of cold milk and transport it to the dental office. Milk helps to preserve the tooth's viability and integrity.
- Saline solution: If milk is not available, use a container of saline solution (e.g., contact lens solution) to store the tooth.
- Do not dry the tooth: Avoid allowing the tooth to dry out, as this can decrease the chances of successful reimplantation.
- Dental Evaluation and Treatment:
- Immediate dental evaluation: The patient should be seen by a dentist or emergency dental care provider as soon as possible, ideally within 30 minutes of the injury.
- Examination and assessment: The dentist will examine the avulsed tooth, assess the extent of damage, and determine the feasibility of reimplantation.
- Cleaning and stabilization: The dentist may clean the tooth and socket, stabilize the tooth with a splint, and prescribe antibiotics or pain medication as needed.
- Follow-up care: The patient will require follow-up appointments to monitor the tooth's healing and assess its long-term viability. Additional dental treatments, such as root canal therapy or dental restoration, may be necessary depending on the extent of damage.
- Long-Term Management:
- Monitor healing: The patient should follow the dentist's instructions for post-reimplantation care, including oral hygiene practices and dietary modifications.
- Regular dental visits: Schedule regular follow-up appointments with the dentist to monitor the tooth's healing, assess its stability, and address any complications or concerns.
- Considerations for children: In cases of tooth avulsion in children with primary (baby) teeth, reimplantation may not be possible or advisable. However, prompt dental evaluation is still essential to assess for associated injuries and prevent complications.
In summary, tooth avulsion is a dental emergency that requires prompt and appropriate management to maximize the chances of successful reimplantation and long-term tooth survival. Immediate response, proper storage and transport of the avulsed tooth, dental evaluation and treatment, and long-term follow-up care are essential components of tooth avulsion management. If you or someone you know experiences tooth avulsion, seek immediate dental care and follow the dentist's instructions for optimal outcomes.
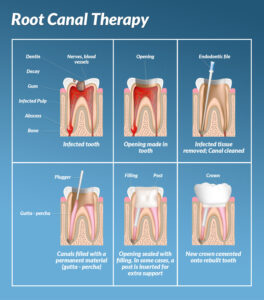
Endodontic Therapy
Endodontic therapy, commonly known as root canal treatment, is a dental procedure designed to treat infections, injuries, or damage to the dental pulp (the soft tissue inside the tooth) and surrounding tissues. The goal of endodontic therapy is to save a tooth from extraction by removing the infected or inflamed pulp, cleaning and disinfecting the root canal system, and sealing it to prevent further infection. Here's an overview of the endodontic therapy process:
- Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- The process begins with a thorough examination by a dentist or endodontist (a dentist specializing in root canal treatment). Symptoms such as toothache, sensitivity to hot or cold, swelling, or gum tenderness may indicate the need for endodontic therapy. X-rays or other imaging tests may be used to assess the extent of damage and determine the best course of treatment.
- Local Anesthesia:
- Before the procedure begins, local anesthesia is administered to numb the affected tooth and surrounding tissues, ensuring that the patient remains comfortable and pain-free throughout the treatment.
- Access Opening:
- Once the tooth is numb, the dentist creates a small access opening in the top of the tooth, usually through the biting surface (occlusal) or back of the tooth (lingual/palatal), to gain access to the pulp chamber and root canals.
- Pulp Removal:
- Using specialized instruments called endodontic files, the dentist carefully removes the infected or inflamed pulp tissue from the pulp chamber and root canals. The root canals are cleaned and shaped to remove any debris, bacteria, or infected tissue.
- Root Canal Disinfection:
- The root canals are thoroughly irrigated with antimicrobial solutions to disinfect and flush out any remaining bacteria or debris. This helps eliminate infection and reduce the risk of reinfection.
- Filling and Sealing:
- Once the root canals are cleaned and disinfected, they are filled with a biocompatible material called gutta-percha to replace the removed pulp tissue and seal the canals to prevent bacteria from re-entering. The access opening is then sealed with a temporary or permanent filling.
- Restoration:
- After the root canal treatment is completed, the tooth may require a permanent restoration such as a dental crown to protect and strengthen the tooth's structure. The crown restores the tooth's appearance, function, and integrity, allowing it to withstand normal biting and chewing forces.
- Follow-Up Care:
- Following endodontic therapy, patients may experience some mild discomfort or sensitivity, which can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medications. It's essential to follow any post-operative instructions provided by the dentist and attend any recommended follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and the long-term success of the treatment.
Endodontic therapy is highly successful in saving teeth that would otherwise need to be extracted due to infection or damage. With advancements in techniques and technology, root canal treatment has become more comfortable, efficient, and predictable, allowing patients to preserve their natural teeth and maintain optimal oral health.