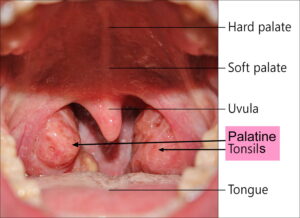
What is it?
Lingual tonsillitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the lingual tonsils, which are clusters of lymphoid tissue located at the base of the tongue. Similar to the palatine tonsils (commonly referred to as the tonsils), the lingual tonsils play a role in the immune system’s defense against infections.
Here are some key points about lingual tonsillitis:
- Causes: Lingual tonsillitis is typically caused by viral or bacterial infections. Common viral pathogens responsible for lingual tonsillitis include the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), adenovirus, or influenza virus. Bacterial infections, particularly streptococcal bacteria (such as Streptococcus pyogenes), can also cause lingual tonsillitis. Other potential causes include fungal infections, allergies, or irritants (such as smoking or environmental pollutants).
- Symptoms: The symptoms of lingual tonsillitis are similar to those of tonsillitis affecting the palatine tonsils. These may include sore throat, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), pain or discomfort at the back of the tongue, swollen or enlarged lingual tonsils, redness or inflammation of the throat, fever, headache, or swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis of lingual tonsillitis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and evaluation of symptoms. The healthcare provider may examine the back of the throat and base of the tongue using a lighted instrument called a tongue depressor or perform a throat culture or swab to identify the causative organism. Imaging studies such as CT scan or MRI may be ordered in cases of severe or recurrent lingual tonsillitis to assess for complications or underlying structural abnormalities.
- Treatment: Treatment of lingual tonsillitis aims to alleviate symptoms, eliminate the underlying infection, and prevent complications. This may involve conservative measures such as rest, hydration, warm saltwater gargles, throat lozenges, or over-the-counter pain relievers (such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen) to relieve discomfort. In cases of bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy may be prescribed. For fungal infections or severe cases of lingual tonsillitis, antifungal medications or corticosteroids may be recommended.
- Complications: If left untreated, lingual tonsillitis can lead to complications such as peritonsillar abscess (collection of pus near the tonsils), retropharyngeal abscess (infection in the deep tissues of the neck), or airway obstruction due to swelling of the lingual tonsils. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent complications and promote recovery.
In summary, lingual tonsillitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the lingual tonsils, characterized by symptoms such as sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and swollen lingual tonsils. Treatment typically involves conservative measures and, in some cases, antibiotic therapy to eliminate the underlying infection and alleviate symptoms. Prompt medical attention is important to prevent complications and promote recovery.