What is it?
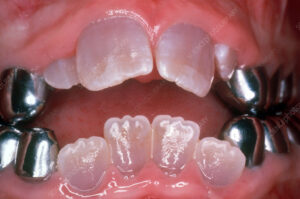
Dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI) is a hereditary genetic disorder that affects the development and formation of dentin, one of the primary tissues that make up teeth. It is characterized by abnormal dentin structure and composition, leading to weakened and discolored teeth that are prone to fracture, wear, and sensitivity. Dentinogenesis imperfecta is typically inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, meaning that a child has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition if one of their parents carries the mutated gene.
Here are some key points about dentinogenesis imperfecta:
- Types: Dentinogenesis imperfecta is classified into three main types based on clinical and genetic features:
- Type I: Also known as classic or hereditary opalescent dentinogenesis imperfecta, this type is the most common and severe form of the condition. It is characterized by translucent or opalescent (bluish-gray) teeth with bulbous crowns, narrow roots, and severe attrition (wear) of the enamel. Type I DI is caused by mutations in the DSPP (dentin sialophosphoprotein) gene, which encodes a protein involved in dentin formation.
- Type II: Also known as coronal dentinogenesis imperfecta, this type is characterized by similar dental abnormalities as type I DI but with less severe enamel involvement. Teeth may appear yellow-brown or amber in color and may be more resistant to fracture compared to type I DI. Type II DI is also caused by mutations in the DSPP gene.
- Type III: Also known as Brandywine type dentinogenesis imperfecta, this type is characterized by similar dental abnormalities as type II DI but with additional skeletal abnormalities such as short stature and joint laxity. Type III DI is caused by mutations in the DSPP gene as well.
- Clinical Presentation: Dentinogenesis imperfecta typically presents with a distinctive appearance of the teeth, including opalescent or discolored enamel, bulbous crowns, and attrition of the enamel exposing the underlying dentin. The teeth may appear translucent or amber in color, and the enamel may chip or fracture easily due to its weakened structure. Individuals with dentinogenesis imperfecta may also experience dental sensitivity, pulp exposure, and increased risk of dental caries and infections.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis of dentinogenesis imperfecta is based on clinical and radiographic findings, including characteristic dental abnormalities such as opalescent or discolored enamel, bulbous crowns, and narrowed pulp chambers. Dental X-rays may reveal thin and bulbous roots, obliteration of the pulp chambers, and dentin defects such as taurodontism (enlarged pulp chambers) or pulpal calcifications. Genetic testing may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and identify the underlying genetic mutation responsible for the condition.
- Treatment: Treatment of dentinogenesis imperfecta focuses on preserving tooth structure, preventing complications, and improving oral function and aesthetics. Management options may include dental restorations such as crowns, veneers, or composite fillings to protect and reinforce weakened teeth, extraction of severely affected teeth followed by prosthetic replacement, endodontic therapy (root canal treatment) for teeth with pulp exposure or infection, and preventive measures such as fluoride therapy and meticulous oral hygiene to reduce the risk of dental caries and infections.
In summary, dentinogenesis imperfecta is a hereditary genetic disorder characterized by abnormal development and structure of dentin, resulting in weakened and discolored teeth that are prone to fracture, wear, and sensitivity. Early diagnosis and appropriate dental management are essential for preserving tooth structure, preventing complications, and improving oral function and aesthetics in individuals with dentinogenesis imperfecta.