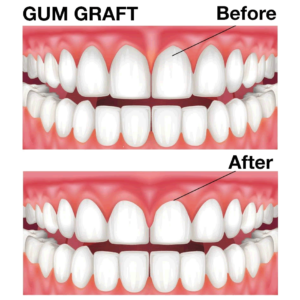
What is it?
Gum graft surgery, also known as gingival grafting or periodontal plastic surgery, is a procedure aimed at treating gum recession and improving the health and appearance of the gums. Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing the tooth roots and potentially leading to tooth sensitivity, root decay, and aesthetic concerns. Gum graft surgery involves harvesting tissue from another area of the mouth, typically the palate (roof of the mouth), and transplanting it to the receded gum area to restore gum volume and coverage. Here’s an overview of gum graft surgery and its key aspects:
- Types of Gum Grafts:
- There are several types of gum grafts used in gum graft surgery, including:
- Connective Tissue Graft: The most common type of gum graft, connective tissue graft involves harvesting a small flap of tissue from the palate and suturing it to the area of gum recession. The tissue flap is carefully positioned to cover the exposed tooth roots and integrate with the existing gum tissue.
- Free Gingival Graft: In this technique, a thin layer of tissue is removed directly from the palate and transplanted to the recipient site without creating a flap. Free gingival grafts are often used to increase the thickness of the gum tissue and provide a protective barrier against further recession.
- Pedicle Graft: Pedicle graft, also known as lateral graft, involves repositioning a flap of gum tissue from an adjacent area of the mouth to cover the exposed tooth roots. Unlike other graft types, pedicle grafts remain partially attached to the donor site, allowing for a continuous blood supply.
- Indications for Gum Graft Surgery:
- Gum graft surgery may be recommended for patients with:
- Significant gum recession resulting from periodontal disease, aggressive tooth brushing, trauma, or other factors.
- Increased tooth sensitivity due to exposed tooth roots.
- Aesthetic concerns related to gum recession, such as uneven gum line or “long tooth” appearance.
- Risk of further gum recession and associated complications, including tooth decay and tooth loss.
- Preoperative Evaluation:
- Before gum graft surgery, the patient undergoes a comprehensive dental examination to assess the extent of gum recession, evaluate oral health, and determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Dental X-rays or imaging may be taken to visualize the bone and soft tissue anatomy.
- Surgical Procedure:
- Gum graft surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort during the procedure. The steps involved in the surgery may include:
- Harvesting Tissue: A small section of tissue is carefully removed from the palate or another donor area using a scalpel or specialized surgical instruments.
- Graft Placement: The harvested tissue is transplanted to the recipient site and secured in place using sutures or tissue adhesive. The graft is positioned to cover the exposed tooth roots and create a natural gum line.
- Wound Closure: Once the graft is in place, the surgical site is carefully closed and protected with a periodontal dressing or surgical stent to promote healing and stabilize the graft.
- Postoperative Care and Recovery:
- After gum graft surgery, patients are provided with postoperative instructions and guidelines to facilitate healing and minimize discomfort. This may include:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications or prescription pain relievers may be recommended to manage postoperative pain and discomfort.
- Oral Hygiene: Patients are instructed to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing and flossing around the surgical site, to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Dietary Restrictions: Soft or liquid diet may be advised initially to avoid irritating the surgical site and aid in healing.
- Follow-up Appointments: Patients are scheduled for follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress, remove sutures if necessary, and assess treatment outcomes.
- Long-Term Outcomes:
- The success of gum graft surgery depends on various factors, including the patient’s oral health, adherence to postoperative care instructions, and the type of graft used. With proper treatment and follow-up, gum graft surgery can effectively restore gum volume, reduce tooth sensitivity, and enhance the overall health and aesthetics of the smile. It is essential for patients to maintain regular dental visits and practice good oral hygiene to ensure long-term success and prevent recurrence of gum recession.
In summary, gum graft surgery is a valuable procedure used to address gum recession and improve gum health and aesthetics. By transplanting tissue from one area of the mouth to another, gum graft surgery can help restore lost gum tissue, protect exposed tooth roots, and enhance the overall function and appearance of the smile.