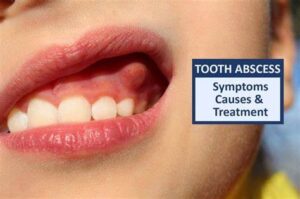
What is it?
A tooth abscess is a painful condition characterized by a collection of pus (a mixture of bacteria, dead tissue, and white blood cells) that forms inside a tooth, in the surrounding gum tissue, or at the root of the tooth. It typically occurs as a result of bacterial infection, often stemming from untreated dental decay, gum disease, or dental trauma. Tooth abscesses can cause severe pain, swelling, and other symptoms, and if left untreated, they can lead to serious complications and spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Here are some key points about tooth abscess:
- Causes:
- Dental decay (caries): Untreated dental cavities can allow bacteria to penetrate deep into the tooth, leading to infection of the dental pulp (the soft tissue inside the tooth).
- Gum disease (periodontitis): Advanced gum disease can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth and creating pockets where bacteria can accumulate and cause infection.
- Dental trauma: Injury to the teeth, such as fractures, cracks, or chips, can expose the pulp to bacteria and lead to infection.
- Previous dental procedures: In some cases, dental procedures such as root canal treatment or tooth extraction may result in infection if bacteria are introduced into the tooth or surrounding tissues.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to dental infections and tooth abscesses.
- Symptoms:
- Severe, throbbing toothache that may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck.
- Swelling and redness of the gums or face, particularly in the area of the affected tooth.
- Sensitivity to pressure or chewing.
- Fever and general malaise (feeling unwell).
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw.
- Foul taste or odor in the mouth.
- Pus drainage or swelling of the lymph nodes if the abscess ruptures.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of a tooth abscess typically involves a clinical examination by a dentist, evaluation of symptoms, and diagnostic tests such as dental X-rays.
- Your dentist will examine the affected tooth and surrounding tissues for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or pus drainage.
- Dental X-rays may be taken to assess the extent of the infection and determine the best course of treatment.
- Treatment:
- Treatment of a tooth abscess aims to eliminate the infection, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
- Drainage of the abscess: Your dentist may drain the pus from the abscess to relieve pressure and pain. This may involve making an incision in the gum tissue or performing a root canal procedure to remove the infected pulp.
- Root canal therapy: In cases where the infection has spread to the dental pulp, root canal therapy may be necessary to remove the infected tissue, clean and disinfect the root canal space, and seal it to prevent further infection.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate the infection and prevent its spread to other parts of the body, particularly if you have a fever or signs of systemic infection.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be recommended to alleviate discomfort and inflammation.
- Follow-up care: Your dentist will monitor your progress and may recommend additional dental treatment, such as a dental crown or extraction, depending on the extent of the damage to the tooth.
- Complications:
- Without prompt treatment, a tooth abscess can lead to serious complications, including:
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body, such as the jawbone, sinuses, or brain.
- Formation of a dental fistula (an opening or channel) through which pus drains from the abscess.
- Development of a dental cyst or granuloma at the site of the abscess.
- Tooth loss or damage to surrounding teeth or bone.
- Prevention:
- To prevent tooth abscesses, it’s important to:
- Practice good oral hygiene habits, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups.
- Avoid consuming sugary or acidic foods and beverages that can contribute to dental decay.
- Seek prompt treatment for dental problems such as cavities, gum disease, or dental trauma.
- Wear protective mouthguards during sports or activities that pose a risk of dental injury.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage underlying medical conditions that may weaken the immune system.
In summary, a tooth abscess is a painful condition characterized by a collection of pus that forms inside a tooth, in the surrounding gum tissue, or at the root of the tooth. It typically occurs as a result of untreated dental decay, gum disease, or dental trauma. Treatment of a tooth abscess involves eliminating the infection, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications through measures such as drainage of the abscess, root canal therapy, antibiotics, and pain management. If you experience symptoms of a tooth abscess, such as severe toothache, swelling, or fever, it’s important to seek prompt dental care to prevent further complications and preserve oral health.